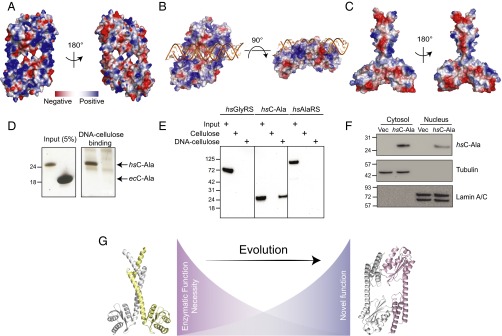
Fig. 4.
Human C-Ala binds DNA. (A) Electrostatic surface views of human C-Ala dimer structure. (B) A DNA-binding model created by ZDOCK program showing that DNA binds to the human C-Ala dimer through the positive charges on surface of the dimer interface. (C) Electrostatic surface views of A. fulgidus C-Ala dimer structure. (D) DNA cellulose-binding assay of Hs C-Ala and Ec C-Ala. (E) DNA cellulose-binding assay of Hs GlyRS, C-Ala and AlaRS. (F) The nuclear distribution of Hs C-Ala. Lamin A/C and tubulin were used as nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) markers, respectively. (G) The distinct dimerization mode for C-Ala during evolution.