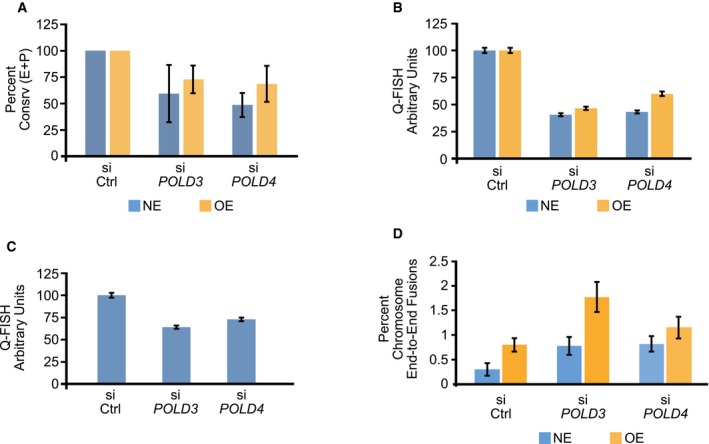
Decrease in the fraction of chromosome arms exhibiting conservative (Consrv) DNA replication of the entire telomere length or part of the telomere (E+P) in U2OS cells after depletion of POLD3 or POLD4 by siRNA. siCtrl, control siRNA; NE, cells expressing normal levels of cyclin E; OE, cells overexpressing cyclin E for 4 days. Bars represent means and standard errors of the mean from two independent experiments. For statistical comparisons, the effects of PolD3 and Pold4 depletion were examined after grouping together the data from the NE and OE cells. PolD3 depletion reduced the fraction of conservatively replicated telomeres at a level of P = 0.072, whereas for PolD4 depletion the decrease was significant at a level of P < 0.025, as calculated using the paired t‐test.
Decreased telomere length following PolD3 or PolD4 depletion in U2OS cells expressing normal levels of cyclin E (NE) or overexpressing cyclin E (OE). The cells were transfected with control siRNA (siCtrl) or siRNAs targeting POLD3 or POLD4 and, 3 days later, fixed and examined for telomere length by Q‐FISH. Bars indicate means and standard error of the mean from more than 2,600 telomeres examined per condition. The differences between control and PolD3‐ or PolD4‐depleted cells were significant (P < 10−6) for both NE and OE cells, as determined by unpaired t‐tests.
Decreased telomere length following PolD3 or PolD4 depletion in parental U2OS cells. The cells were transfected with control siRNA (siCtrl) or siRNAs targeting POLD3 or POLD4 and, 3 days later, fixed and examined for telomere length by Q‐FISH. Bars indicate means and standard error of the mean from more than 2,800 telomeres examined per condition. The differences between control and PolD3‐ or PolD4‐depleted cells were significant (P < 10−6), as determined by unpaired t‐tests.
Increased frequency of chromosome end‐to‐end fusions following POLD3 or POLD4 depletion. U2OS cells expressing normal levels of cyclin E (NE) or overexpressing cyclin E for 4 days (OE) were transfected with control siRNA (siCtrl) os siRNAs targeting POLD3 or POLD4. For each condition, 25 metaphases were examined (representing about 1,900 high‐quality chromosome arms per condition); the percentage of chromosome fusions was determined for each metaphase and used to calculate means and standard errors of the mean. For statistical analysis, the numbers of chromosome end‐to‐end fusions in the various conditions were compared by chi‐square tests. Cyclin E overexpression led to a higher number of fusions (P < 0.0005); PolD3 and PolD4 depletion also led to a higher number of fusions (P < 0.001 and P < 0.025, respectively).