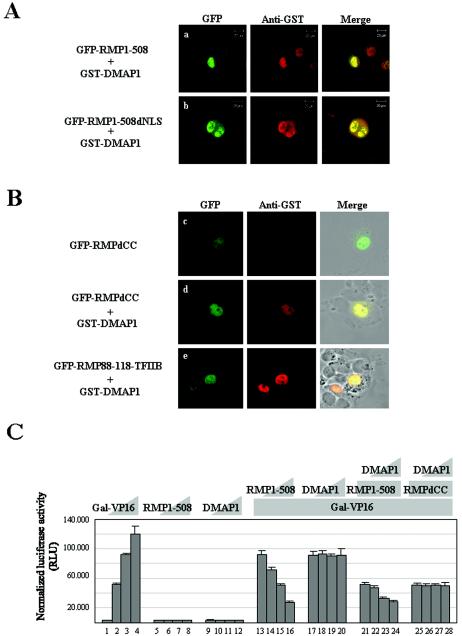
FIG. 7.
DMAP1 facilitates the nuclear localization of RMP and augments corepressor activity of RMP. (A and B) HLE cells were transiently cotransfected with a plasmid expressing GST-DMAP1, along with constructs containing cDNAs of full-length GFP-RMP1-508 (a), GFP-RMP1-508dNLS mutants (b), GFP-RMPdCC (d), and GFP-RMP88-118-TFIIB (e), or HLE cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid expressing GFP-RMPdCC (c). The cells were stained with monoclonal anti-GST antibodies and visualized by Texas Red-linked goat-anti mouse IgGs. The expression of GFP-fused proteins was detected by green fluorescence. (C) A luciferase assay was performed as for Fig. 2B. The cotransfection mixture contained the following constructs: bars 1 to 4, 0, 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 ng of Gal-VP16, respectively; bars 5 to 8, 0, 0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 μg of RMP1-508, respectively; bars 9 to 12, 0, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μg of DMAP1, respectively; bars 13 to 16, 0, 0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 μg of RMP1-508, respectively, plus 0.4 ng of Gal-VP16; bars 17 to 20, 0, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μg of DMAP1, respectively, plus 0.4 ng of Gal-VP16; bars 21 to 24, 0, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μg of DMAP1, respectively, plus 0.4 ng of Gal-VP16 and 0.5 μg of RMP1-508; bars 25 to 28, 0, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μg of DMAP1, respectively, plus 0.4 ng of Gal-VP16 and 0.5 μg of RMPdCC. The error bars indicate standard deviations.