Figure 6.
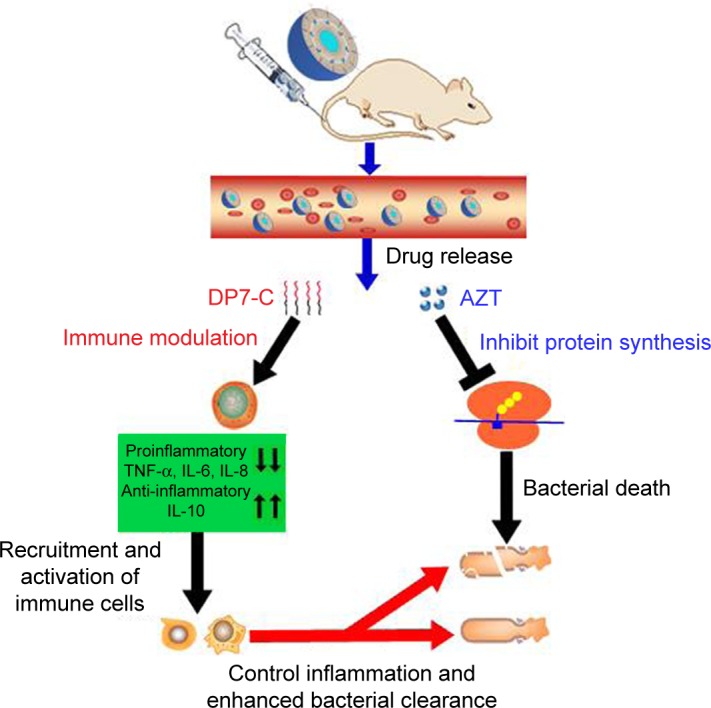
Proposed mechanism of action of AZT-D-LPs.
Notes: Under infected conditions, after IV injection, both DP7-C and AZT were released from AZT-D-LPs formulations. The DP7-C selectively modulates innate immune response, and this results in a supressed inflammatory response that includes the downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8, and a variety of chemokines. Meanwhile, the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was upregulated to neutralize the harmful inflammation, and effector cells and cytokines are recruited to the infection sites and controlled the infections. In addition, the released azithromycin binds the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria and inhibits the bacterial protein synthesis,32–35 resulting in bacterial death, and the DP7-C enhanced innate immune response collaborated with AZT more effectively clear bacterial debris.
Abbreviations: AZT, azithromycin; AZT-D-LPs, DP7-C-modified AZT-loaded liposomes; IL, interleukin; IV, intravenous; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
