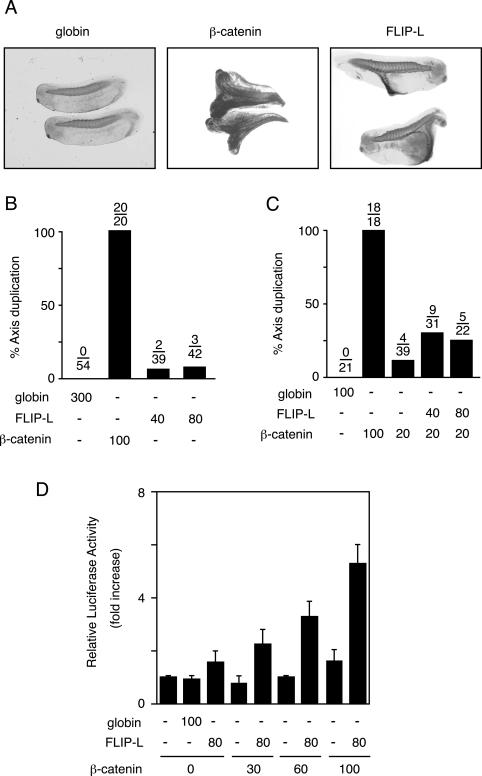
FIG. 8.
Effects of cFLIP-L on Xenopus embryos. (A) Induction of axis duplication by cFLIP-L. Two blastomeres of four-cell stage embryos were injected in the ventral equatorial region with the indicated mRNAs (Xenopus β-globin, 300 ng; mouse β-catenin, 100 ng; cFLIP-L, 40 ng). Axis duplication was validated by ectopic muscle formation, shown by immunostaining using a muscle-specific 12/101 antibody. The embryos were transparentized by benzyl benzoate-benzyl alcohol (2:1). (B) Frequency of axis duplication by cFLIP-L. Xenopus embryos were injected with the indicated mRNAs (the number of nanograms per embryo is shown) as in panel A. The fraction of embryos with a duplicated axis is indicated above each bar. (C) cFLIP-L increases axis duplication induced by suboptimal levels of β-catenin. Xenopus embryos were injected with the indicated mRNAs (the number of nanograms per embryo is shown) as in panel A. The fraction of embryos with a duplicated axis is indicated above each bar. (D) cFLIP-L enhances β-catenin-mediated gene expression in Xenopus embryos. Xenopus embryos were injected with the indicated mRNAs (the number of nanograms per embryo is shown) as in panel A, along with TOP-TK-Luc and pRL-TK. The animal caps were dissected and cultured at 18°C for 24 h in modified Barth's solution containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin. The luciferase activity in the cell lysates from three animal caps was measured and expressed as the increase (n-fold) compared with the level observed in the cells injected with TOP-TK-Luc and pRL-TK. The data represent means of triplicate determinations. The bars indicate standard errors of the mean.