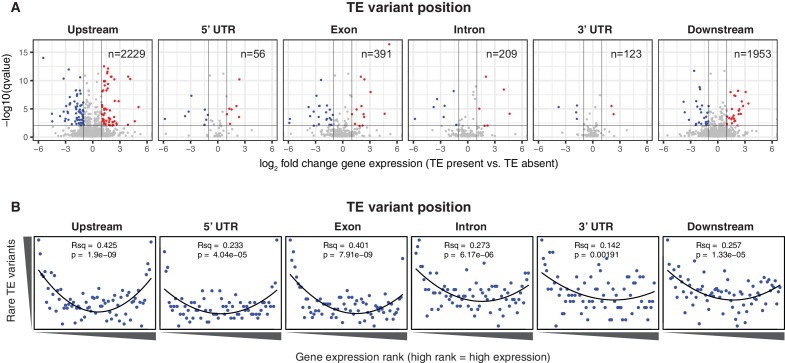
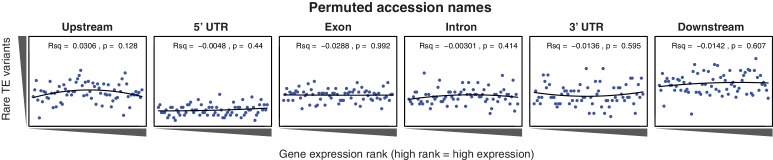
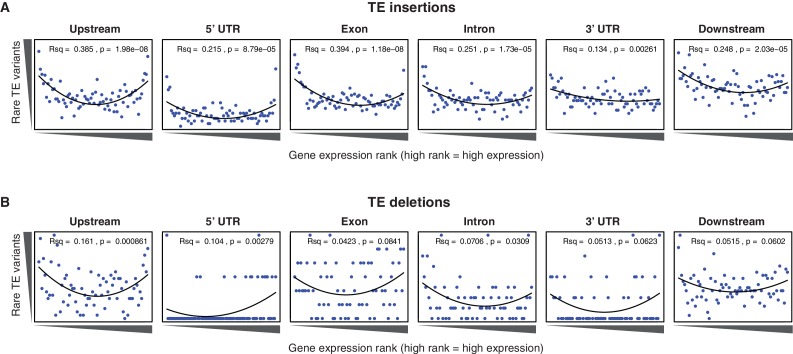
Figure 4. Differential transcript abundance associated with TE variant presence/absence.
(A) Transcript abundance differences for genes associated with TE insertion variants at different positions, indicated in the plot titles. Genes with significantly different transcript abundance in accessions with a TE insertion compared to accessions without a TE insertion are colored blue (lower transcript abundance in accessions containing TE insertion) or red (higher transcript abundance in accessions containing TE insertion). Vertical lines indicate ±2 fold change in FPKM. Horizontal line indicates the 1% false discovery rate. (B) Relationship between rare TE variant counts and gene expression rank. Cumulative number of rare TE variants in equal-sized bins for gene expression ranks, from the lowest-ranked accession (left) to the highest-ranked accession (right). Lines indicate the fit of a quadratic model.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.20777.025