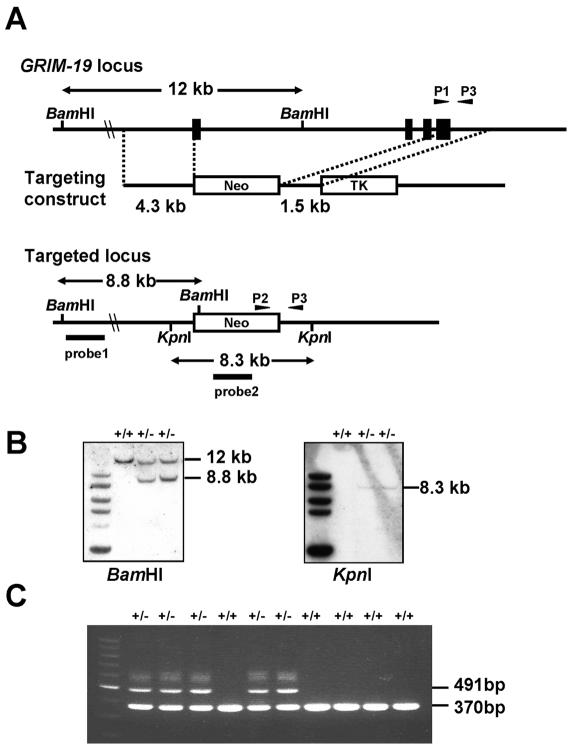
FIG. 1.
Disruption of the murine GRIM-19 gene. (A) Schematic presentation of wild-type and targeted GRIM-19 alleles and the gene targeting construct. Four exons are indicated with closed boxes. Arrowhead P1 indicates the primer specific for the wild-type allele, P2 indicates the primer for the GRIM-19− allele, and P3 indicates the primer for both the wild-type and GRIM-19− alleles. Probes 1 and 2 are used for Southern blot analysis. Neo, neomycin resistance cassette; TK, thymidine kinase marker. (B) Southern blot analysis of targeted ES cells. Genomic DNA from individual ES clones were digested with BamHI or KpnI and analyzed by Southern blotting with probe 1 (left panel) or probe 2 (right panel). The targeted clones are shown with the wild-type (12-kb) and mutant (8.8-kb) fragments as marked. (C) PCR genotyping of offspring from intercrossing two GRIM-19+/− mice. A 370-bp wild-type band and a 491-bp mutant band were amplified by primer pairs P1-P3 and P2-P3, respectively, as indicated in the legend of panel A.