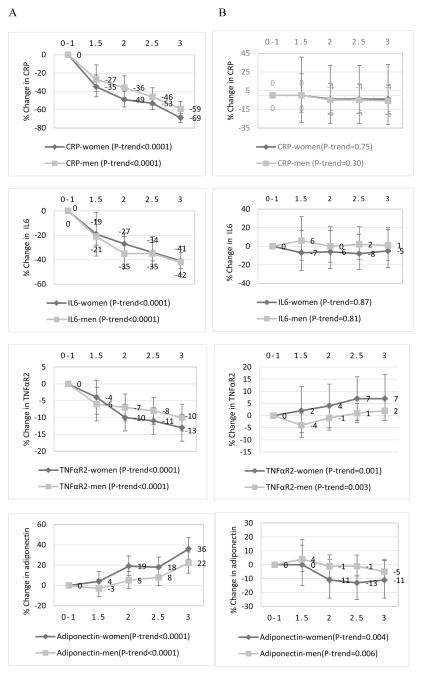
Figure 1.
Multivariable-adjusted percent changes in the relative concentrations of plasma inflammation markers (95% confidence intervals) across adherence categories of (A) the energy balance-related recommendations (BMI, physical activity and energy density), and (B) the combined plant/animal food/alcohol intake recommendations in the Nurses’ Health Study (women), 1990; and Health Professional Follow-up Study (men), 1994. 0–1 was the lowest or least adherent category (reference) while 3 was the highest or most adherent category. CRP=C-reactive protein, IL6=interleukin-6, TNFαR2=tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 2. Biomarker concentrations were adjusted for regular aspirin/NSAID use, age at blood draw, smoking status, physical activity, case-control status, postmenopausal status, postmenopausal hormone use, and chronic diseases/conditions. The following chronic diseases/conditions (yes=1/no=0) were included in the score: hypercholesterolemia, cancer, diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and rheumatoid/other arthritis). The P-value for trend was the P-value of the combined recommendation score as a continuous variable adjusted for all covariates previously listed. Biomarker sample sizes were different: in women, n=3,550 for all four inflammatory markers. In men; CRP, n=5,157; IL6, n=3,044; TNFαR2, n=4,072; and adiponectin, n=4,348.