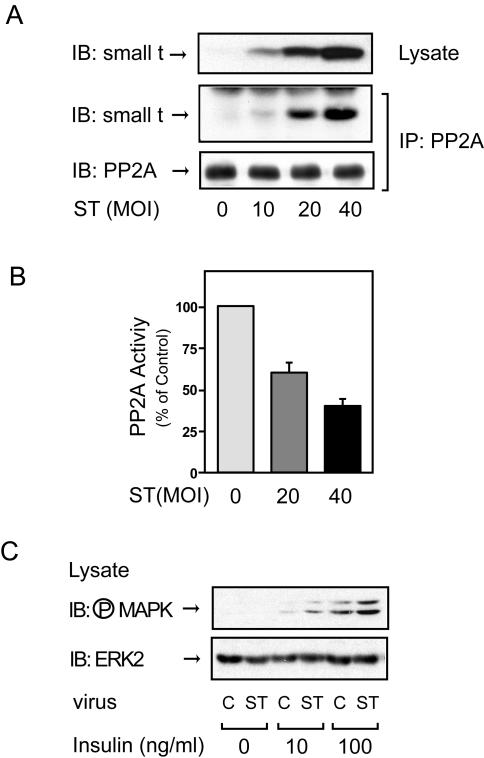
FIG. 1.
Expression of small t antigen inhibits endogenous PP2A activity and enhances insulin-stimulated MAP kinase phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. (A) 3T3-L1 adipocytes infected with small-t-antigen-encoding adenovirus (ST) at the indicated MOIs, as described in Materials and Methods, were lysed, and whole-cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-small t antigen antibody (top panel). The same lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PP2A antibody, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-small t antigen antibody (middle panel) or anti-PP2A antibody (bottom panel). Control studies showed that the antibody (directed against the PP2A C subunit) precipitates intact PP2A. (B) 3T3-L1 adipocytes infected with small-t-antigen-encoding adenovirus at the indicated MOIs were lysed and assayed for PP2A activity. Data are presented as the percentage of phosphatase activity compared to that of uninfected cells and show the mean ± the standard error (SE) of results from four independent experiments. (C) 3T3-L1 adipocytes were infected with small-t-antigen-encoding adenovirus at an MOI of 40 and stimulated with insulin for 5 min, and whole-cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with phospho-specific MAP kinase antibody (upper panel) or anti-ERK-2 antibody (lower panel). C, control.