Figure 6.
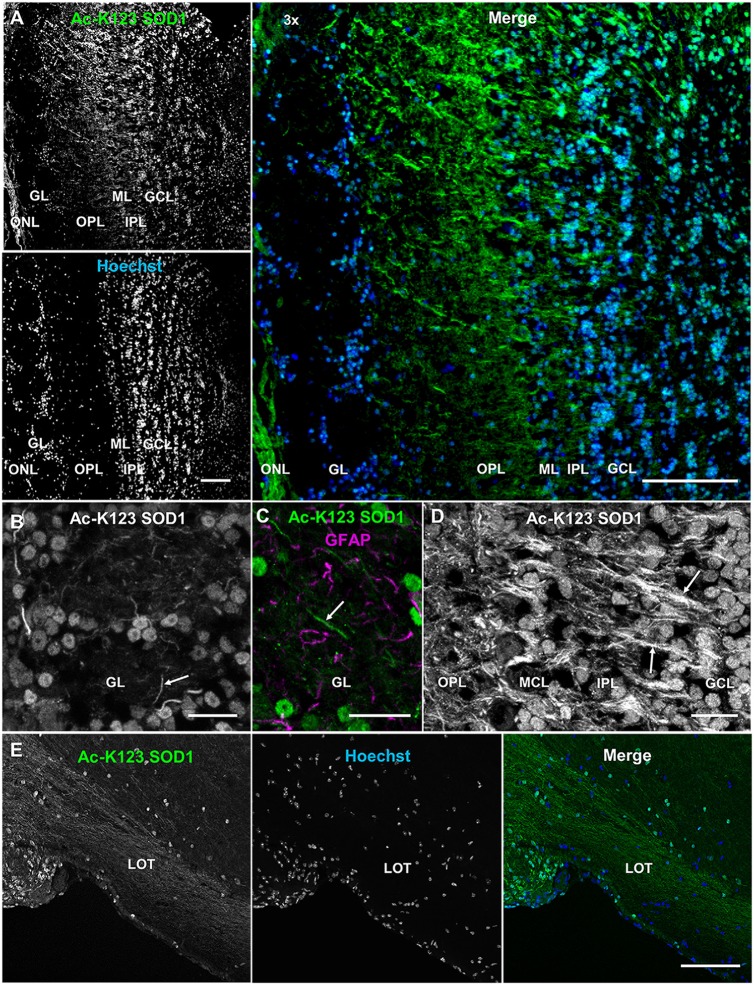
Ac-K123 SOD1 within the olfactory bulb and lateral olfactory tract (LOT). (A) Confocal micrograph (scale bar, 100 μm) showing Ac-K123 SOD1 (R26) immunostaining, Hoechst nuclear counterstaining and 3× merged image of the posterior main olfactory bulb in the coronal plane. Identified regions include olfactory nerve layer (ONL), glomerular layer (GL), outer plexiform layer (OPL), mitral cell layer (MCL), inner plexiform layer (IPL) and granule cell layer (GCL). (B) Confocal micrograph (scale bar, 20 μm) of GL immunostained for Ac-K123 SOD1 (R26). An example of a neurite extending into the glomerulus is also labeled (arrow). (C) Confocal micrograph (scale bar, 20 μm) of an olfactory glomerulus core within the GL labeled for Ac-K123 SOD1 (R26) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). An example of a neurite labeled with Ac-K123 SOD1 and not GFAP is shown (arrow). (D) Confocal micrograph of the OPL, ML, IPL and GCL immunostained for Ac-K123 SOD1 (R26; scale bar, 20 μm). Granule cell processes and tufted or mitral cell primary axons are labeled (arrows). (E) Sagittal view confocal micrograph (scale bar, 100 μm) of posterior olfactory bulb showing axonal tracts extending through the LOT in the area of the olfactory peduncle. Immunostaining of olfactory bulb was performed with antibodies against Ac-K123 SOD1 (R26) and nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342.