Figure 9.
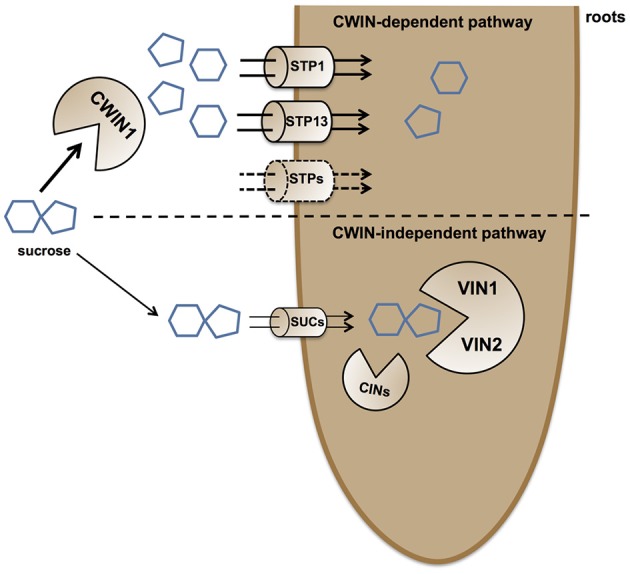
Simplified model of external sucrose retrieval from the surrounding environment. At the root/environment interface, sucrose can be absorbed through two independent pathways. The main route for sucrose assimilation is driven by a AtCWIN1-dependent pathway, resulting in sucrose hydrolysis into glucose and fructose. Hexoses are then taken up by the coordinated activity of hexose specific transporters, such as AtSTP1 and AtSTP13. The alternative CWIN-independent pathway relies on sucrose transporters (most likely AtSUCs) for sucrose internalization and the involvement of intracellular invertases (VINs and CINs) for the generation of free hexoses to support the plant primary metabolism. The vacuole is not shown.
