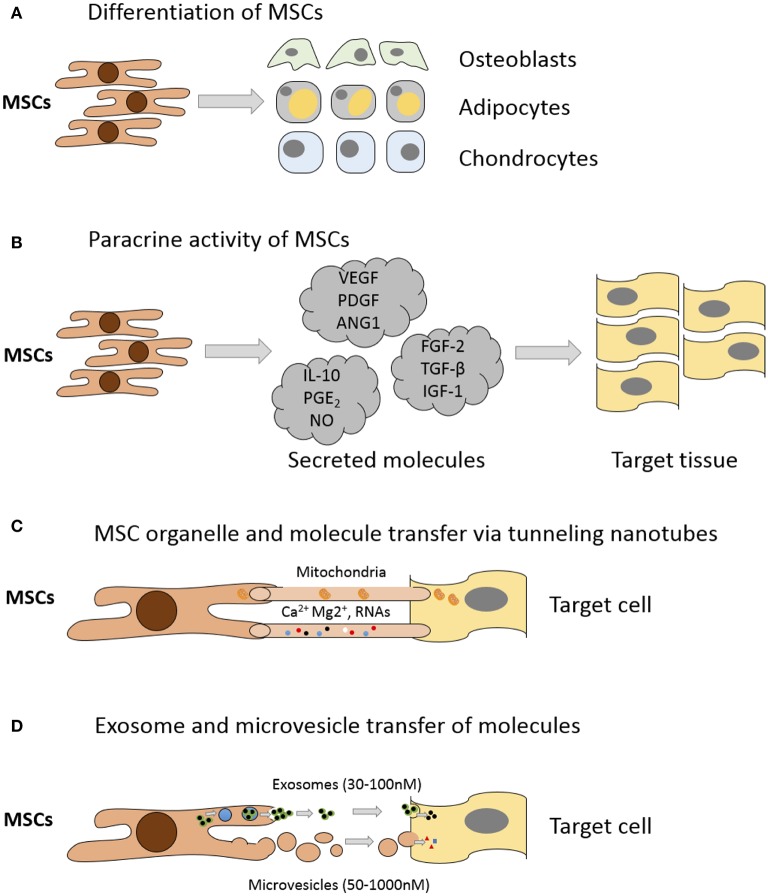
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of MSC mediated repair. (A) Differentiation into replacement cell types. (B) Secretion of paracrine factors such as growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), angiopoietin-1 (ANG1), interleukin-10 (IL-10), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), nitrous oxide (NO), fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2), Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). (C) Transfer of organelles (e.g., mitochondria) and/or molecules through tunneling nanotubes. (D) Transfer of proteins/peptides, RNA, hormones, and/or chemicals by extracellular vesicles such as exosomes or microvesicles. Exosomes are generated through the endocytic pathway and released through exocytosis. Microvesicles are produced by cell surface budding and released directly from the plasma membrane. Adapted from Spees et al. (2016).