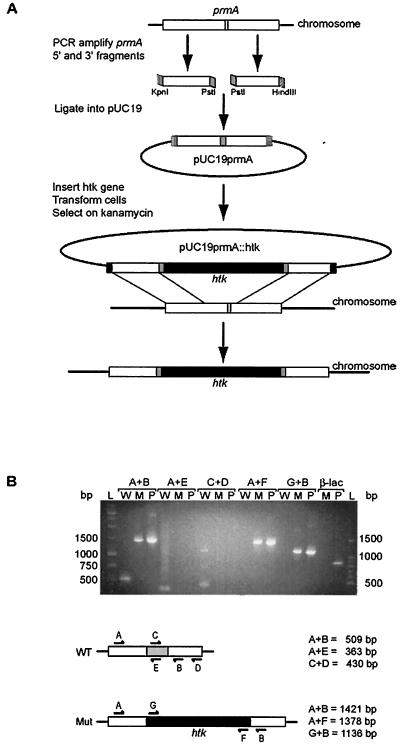
FIG. 1.
Construction of T. thermophilus prmA null mutant. (A) Approximately 165 bp of the wild-type prmA gene (white) containing the SAM binding motif (light gray) was replaced by the heat-stable kanamycin resistance gene (htk; black). KpnI restriction sites are indicated by vertical lines, HindIII restriction sites are indicated by horizontal lines, and PstI restriction sites are indicated in gray. The resulting T. thermophilus strain was designated TLK90. (B) Diagnostic PCRs to confirm disruption of the prmA gene in strain TLK90. Genomic DNA from either wild-type HB8 (W), the null mutant (M), or plasmid pUC19prmA::htk (P) was used as a template for PCRs. The primer sets used for each reaction (A to G) are indicated and shown schematically along with the expected product sizes. The region of the prmA gene that was deleted from the null mutant is represented schematically in gray, and the htk gene is indicated in black. Amplification of the β-lactamase gene (β-lac) from the plasmid template but not from TLK90 genomic DNA template confirmed the absence of this plasmid-derived ampicillin resistance marker gene in the null mutant. Molecular weight DNA ladders are shown (L), and their sizes are indicated in base pairs.