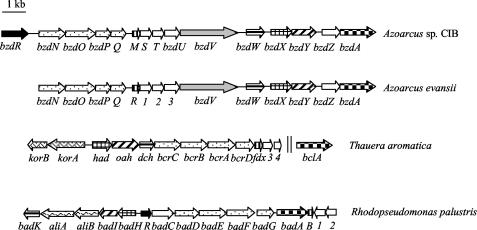
FIG. 4.
Organization of the gene clusters involved in the anaerobic catabolism of benzoate in Azoarcus sp. strain CIB, A. evansii (accession no. AJ428529) (31), T. aromatica (accession no. AJ224959 and AF373594), and R. palustris (accession no. U75363). Genes are represented by arrows as follows: black, regulatory genes; white, genes of unknown function; checkerboard pattern, genes encoding the benzoate-CoA ligases; stippling, genes encoding the four subunits of the benzoyl-CoA reductase; vertical stripes, ferredoxins; horizontal stripes, genes encoding enoyl-CoA hydratases; cross hatching, genes encoding NAD-dependent dehydrogenases; hatching, genes encoding ring-cleavage hydrolases; gray, gene encoding a putative ferredoxin oxidoreductase; wavy, genes encoding enzymes of alicyclic acid degradation; intertwined lines, genes encoding the 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase. Two vertical lines indicate that the genes are not adjacent in the genome.