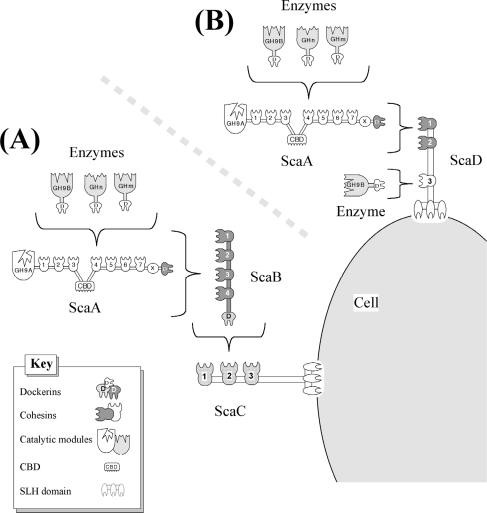
FIG. 6.
Schematic model of the proposed interactions among the A. cellulolyticus cellulosomal components and the two modes of attachment to the cell surface. (A) Dockerin-containing enzymes are incorporated into the ScaA scaffoldin via interaction with the ScaA cohesins. The ScaA dockerin binds to the ScaB type II cohesins, and the ScaB dockerin binds to the ScaC cohesins. The latter complex is anchored to the cell surface by the ScaC SLH module. This arrangement was described by Xu et al. (57). (B) In the additional mechanism of attachment, the enzyme-laden ScaA is bound to the type II cohesins of ScaD, which can also accept a single enzyme via its third type I cohesin. The SLH module of ScaD serves to anchor the alternative complex to the cell surface.