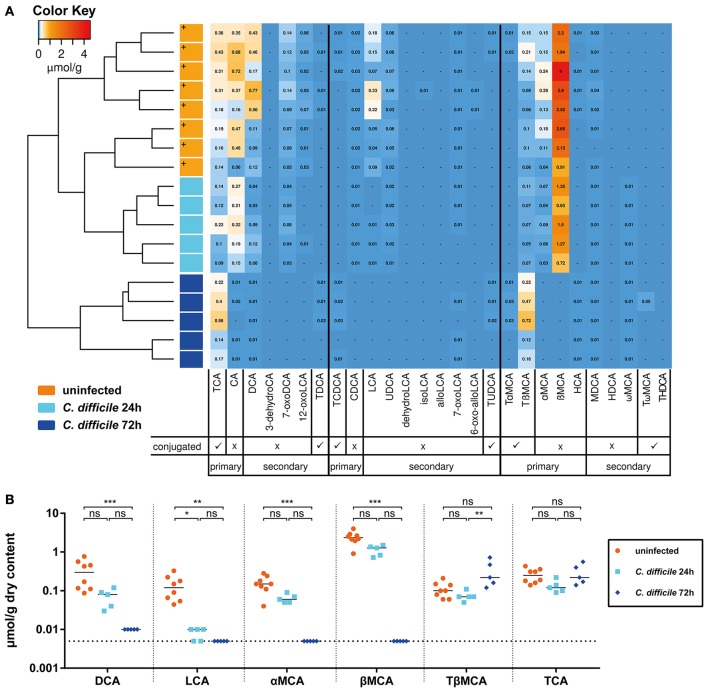
Figure 4.
Infection of sDMDMm2 + C. scindens mice with C. difficile leads to decrease in secondary and deconjugated primary bile acids. Cecal contents of sDMDMm2 + C. scindens mice infected with C. difficile used in Figure 3 were used to quantify bile acid measurements. Measurements from uninfected control mice (colonized with C. scindens for 7 days) from Figure 2 were included as comparison (orange symbols, indicated by plus sign). (A) Heatmap analysis constructed from bile acid LC-MS/MS measurements. Values indicate measured bile acid concentrations in μmol/g dry weight of cecal content. (B) Analysis of individual bile acids in sDMDMm2 + C. scindens mice infected by C. difficile over time. Statistical analysis used the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post-test to compare individual bile acids between the groups. Each symbol represents one individual. Bars indicate medians. Dotted lines indicate lower limit of detection. ns, not statistically significant (p ≥ 0.05); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. TCA, taurocholic acid; CA, cholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; 3-dehydroCA, 3-dehydrocholic acid; 7-oxoDCA, 7-oxodeoxycholic acid; 12-oxoLCA, 12-oxolithocholic acid; TDCA, taurodeoxycholic acid; TCDCA, taurochenodeoxycholic acid; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; dehydroLCA, dehydrolithocholic acid; isoLCA, iso-lithocholic acid; alloLCA, allo-lithocholic acid; 7-oxoLCA, 7-oxolithocholic acid; TUDCA, tauroursodeoxycholic acid; TαMCA, tauro-α-muricholic acid; TβMCA, tauro-β-muricholic acid; αMCA, α-muricholic acid; βMCA, β-muricholic acid; HCA, hyocholic acid; MDCA, murodeoxycholic acid; 6-oxo-allo-LCA, 6-oxo-allo-lithocholic acid; HDCA, hyodeoxycholic acid; ωMCA, ω-muricholic acid; TωMCA, tauro-ω-muricholic acid; THDCA, taurohyodeoxycholic acid.