FIGURE 6:
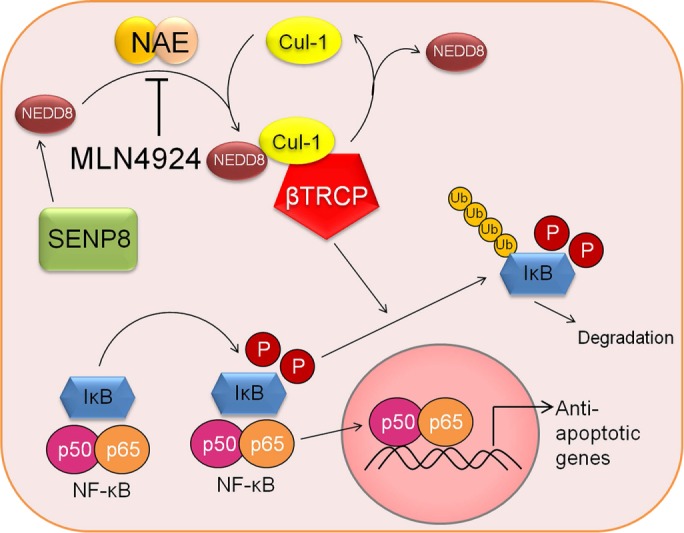
Mechanistic model of the effect of MLN4924 on the NF-κB pathway and downstream apoptotic responses. Under normal conditions, IκB is unphosphorylated and binds NF-κB subunits, sequestering them in the cytoplasm. An inflammatory stimulus leads to the phosphorylation of IκB, which is recognized by the Cul-1-Nedd8-transducin repeat–containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (TRCP) complex, targeting IκB for polyubiquitination and degradation by the proteosome. NF-κB can then translocate into the nucleus, leading to the transcription of target genes, including antiapoptotic cascades. Pharmacological inhibition of Cul-1 neddylation using MLN4924 stabilizes cellular IκB levels, keeping NF-κB out the nucleus and leading to decreased transcription of antiapoptotic target genes and increased apoptosis.
