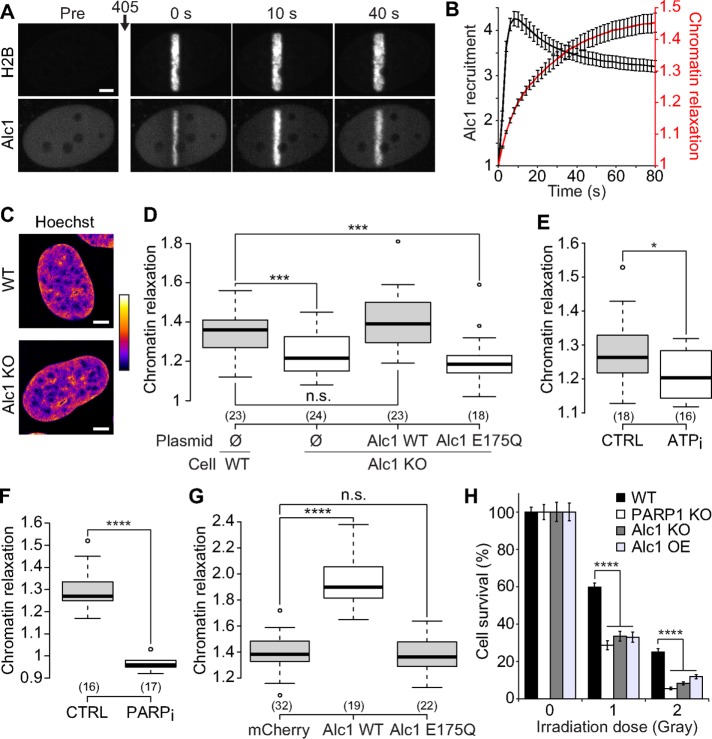
FIGURE 5:
The chromatin remodeler Alc1 contributes to chromatin relaxation upon DNA damage. (A) Confocal image sequence of a U2OS nucleus coexpressing H2B-PAGFP and Alc1-mCherry. Scale bar: 4 μm. (B) Relative kinetics of Alc1 recruitment and chromatin relaxation at the DNA lesions measured in Alc1 KO cells coexpressing H2B-PAGFP and Alc1-mCherry (mean ± SEM, n = 20). (C) Confocal images of wild-type and Alc KO U2OS cells labeled with Hoechst. Scale bar: 4 μm. Fluorescence signals are pseudocolored using the lookup table shown on the right of the images. (D) Relative chromatin relaxation at 60 s after laser microirradiation for wild-type vs. Alc1 KO cells cotransfected with H2B-PAGFP and an empty plasmid (Ø), wild-type Alc1 or the catalytic-dead mutant Alc1 E175Q, both fused to mCherry. Cells with comparable expression levels of the wild-type or mutant Alc1 constructs were chosen, as assessed by similar fluorescence signals in the mCherry channel. (E) Relative chromatin relaxation at 60 s after laser microirradiation in Alc1 KO cells expressing H2B-PAGFP and depleted or not for ATP. (F) Relative chromatin relaxation at 60 s after laser microirradiation in Alc1 KO cells expressing H2B-PAGFP and treated or not with the PARP1 inhibitor AG14361 (30 μM, 1 h). (G) Relative chromatin relaxation at 60 s after laser microirradiation for wild-type cells expressing H2B-PAGFP and transfected with uncoupled mCherry, wild-type Alc1 fused to mCherry, or the catalytic-dead mutant Alc1 E175Q fused to mCherry. Cells with comparable expression levels of the transfected constructs were chosen, as assessed by similar fluorescence signals in the mCherry channel. (H) Clonogenic survival after different doses of X-ray irradiation for wild-type U2OS cells, KOs for Alc1 and PARP1, and wild-type cells overexpressing Alc1 fused to YFP.