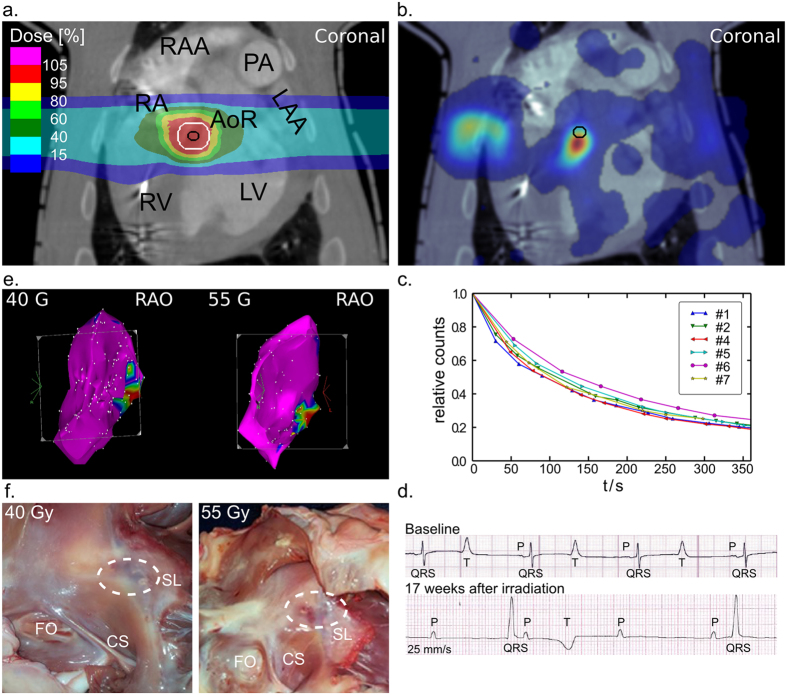
Figure 1. Application of Carbon Ions for Atrioventricular Junction Ablation.
(a) Coronal view of a treatment plan for irradiation of the atrioventricular junction. Dose depicted as color-wash, the target contour is shown in black, the enlarged target contour in white. 100% corresponds to the prescribed dose of 55 Gy. (b) Image of positron emission tomography after 55 Gy of carbon, projected over the coronal plane of a contrast-enhanced CT scan; the target contour is shown in black. (c) Decay of the detected ß+-signal over the course of six minutes. (d) Surface ECG (25 mm/sec) before irradiation and 17 weeks after irradiation. (e) Right anterior oblique (RAO) projection of right atrial electroanatomical voltage maps obtained via an intracardiac catheter with point-by-point sampling after ablation. Voltage legend is shown next to the image; local voltage >1.0 mV depicted in magenta. Voltage <0.5 mV depicted in red. Other colors mark voltages in-between. (f) Right lateral views of lesion outcomes at the tricuspid annulus; dashed lines mark the respective lesion location. AoR = Aortic root; CS = Ostium of coronary sinus; FO = Fossa ovalis; LAA = Left atrial appendage; LV = Left ventricle; PA = Pulmonary artery; RA = Right atrium; RV = Right ventricle; SL = Septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve.