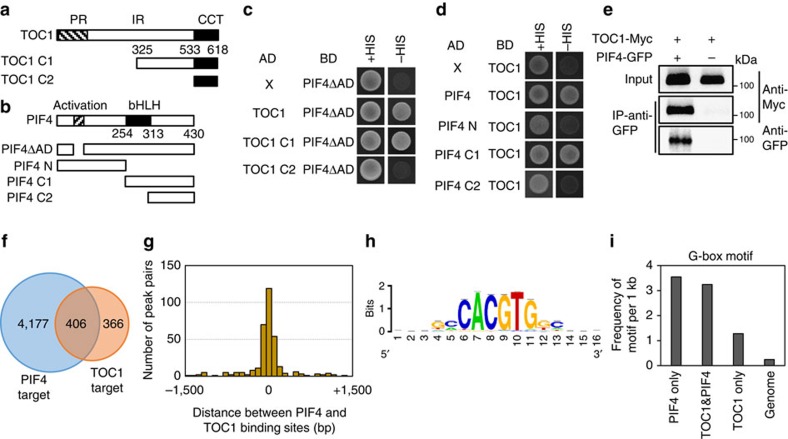
Figure 1. TOC1 directly interacts with PIF4.
(a,b) Box diagram of various fragments of PIF4 and TOC1 used in c,d. (c,d) Yeast two-hybrid assays. Yeast clones were grown on the synthetic dropout medium (+HIS) or synthetic dropout medium without histidine plus 1 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-Triazol (3-AT) (−HIS). The experiments were replicated with additional yeast clones (Supplementary Fig. 1). (e) Co-IP assays. Protein extracts from protoplasts expressing TOC1-Myc or TOC1-Myc and PIF4-GFP were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and analysed by immunoblottings with anti-GFP or anti-Myc antibody. The molecular weight (kDa) is indicated on the right side of the gel. (f) Overlap between target genes of PIF4 and TOC1 identified in the previous ChIP-Seq studies9,19 is statistically significant (Fisher's exact test P<2 × 10−16). (g) Distribution of distances between the binding sites of PIF4 and TOC1 in their common target genes identified in f. (h) The most enriched motif in the TOC1-binding sites of the PIF4 and TOC1 common target genes. (i) Frequency of G-box motif per 1 kb in the PIF4-specific binding sites (PIF4 only) and TOC1-binding sites of the PIF4 and TOC1 common target genes (TOC1 & PIF4) or TOC1-specific target genes (TOC1 only).