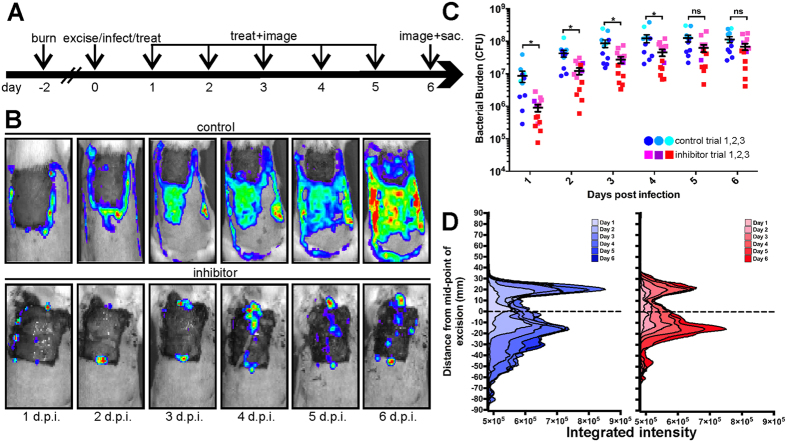
Figure 2. Treatment of excised burn wounds with a GST-MAM beads decreases bacterial burden and spatially constrains the spread of infection.
(A) Schematic of infection and dosing schedule. (B) Representative bioluminescence images of control bead treated (upper row) or MAM7 inhibitor treated (bottom row) P. aeruginosa infected excisions over 6 days after infection (d.p.i.). (C) Quantification of bacterial loads in control bead-treated (shades of blue) and inhibitor treated (shades of red) animals using IVIS biophotonic imaging. Different shading indicates three sets of independent trials. Data for individual animals, means ± s.e.m. for each treatment group are depicted. Analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, was used to test for significance. (*) indicates p ≤ 0.05, ns, not significant. (D) Quantitative analysis of the spread of infection to adjacent tissues.