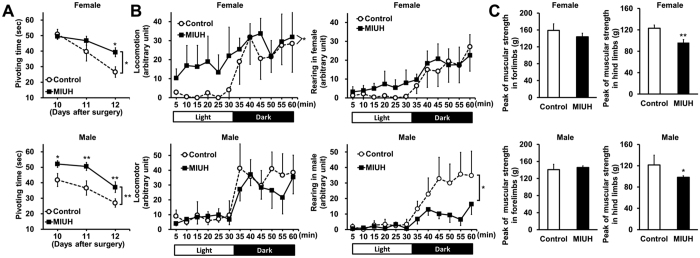
Figure 3. Behavioral tests.
(A) To examine neonatal reflexes, negative geotaxis tests were performed on three consecutive days from 10 to 12 days after the surgery (control group, female n = 8 and male n = 10; MIUH group, female n = 17 and male n = 22). The development of neonatal reflexes in female and male pups exposed to mild intrauterine hypoperfusion on E17 (MIUH group) was significantly slower than that of the control pups. (B) To measure spontaneous activity, P15 rats were subjected to an open-field test. For locomotor activities (horizontal movements), female rats exposed to MIUH showed significant hyperactivity compared with the activity of control rats in a light environment. For rearing activities (vertical movements), male rats in the MIUH group showed hypoactivity compared with the activity of control rats in a dark environment (control group, female n = 8 and male n = 6; MIUH group, female n = 9 and male n = 12). (C) Muscular strength in the forelimbs and hind limbs was measured using a traction meter on P35. For the hind limbs, muscular strength was significantly lower in the female and male rats exposed to MIUH than in the control rats. For the forelimbs, no clear difference between the two groups was detected (control group, female n = 5 and male n = 3; MIUH group, female n = 9 and male n = 12). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. control group. E, Embryonic day. P, Postnatal day.