Figure 1. Mechanistic pathway of formation of a Hg(II) sulfide dimer by dealkylation38 of two Hg-thiolate complexes.
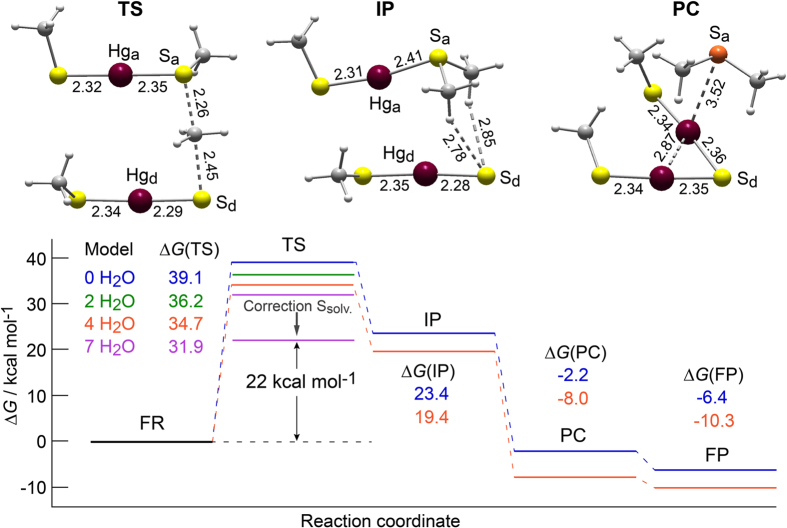
Gibbs free energy diagram (at 298 K and 1 atm) of the cleavage of the S-C bond by an alkyl group transfer between two linear Hg-thiolate complexes, and optimized structures for the reaction pathway with four explicit water molecules (not shown for clarity). The height of the activation-energy barrier for the alkyl group transfer relative to the free reactant state decreases from 39.1 kcal mol−1 to 36.2 kcal mol−1 with two explicit water molecules, to 34.7 kcal mol−1 with four, and to 31.9 kcal mol−1 with seven. The final value, corrected for overestimation of the solvation entropy in the continuum solvation models is 22 kcal mol−1. The same correction applies to the IP and PC states (corrected levels not shown). FR = free reactants; TS = transition state; IP = intermediate product; PC = product complex; FP = free products. Bond lengths are in angstroms. Dark red, Hg; yellow, thiolate sulfur SR− and sulfide sulfur HgSHg; orange, thioether sulfur RSR; dark gray, C; light gray, H. Cartesian coordinates are given in the Supplementary Materials.