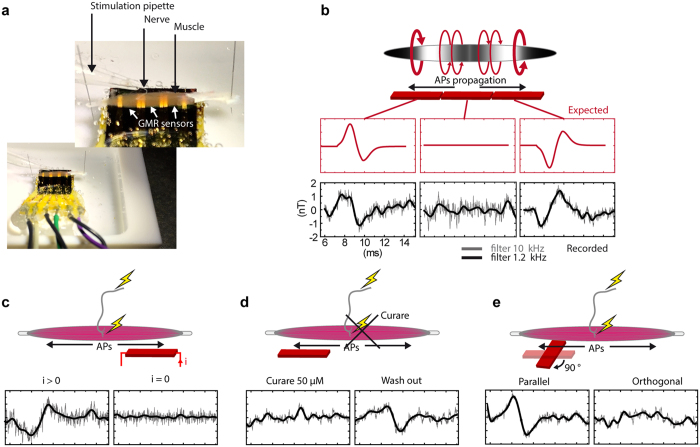
Figure 3. Magnetic recordings.
(a) Photography of the recording chamber, with the muscle held by its tendons on the top of the magnetic probe, and with the nerf sucked into a stimulating glass pipette. (b) Expected and recorded magnetic signal on the three GMR-sensors after electrical stimulation of the nerve. Traces are averages over 500 trials, filtered with a low pass filter at 10 (gray traces) or 1.2 kHz (black traces). (c) In absence of feeding current in the GMR sensor, the absence of electrical signal shows the quality of the electrical insulation and demonstrates that the recorded signal is purely magnetic. (d) MF following nerve stimulation in control conditions, in presence of the reversible synaptic receptors blocker curare, and after wash out. (e) Juxtaposition of the MFs recorded with the muscle held successively orthogonal and parallel with respect to the probe sensitivity orientation.