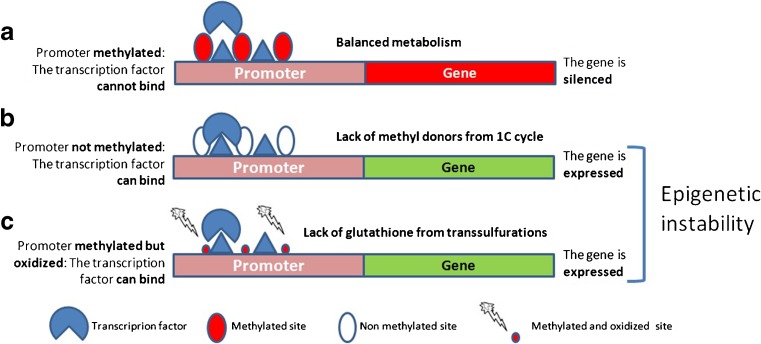
Fig. 1.
Epigenetic instability from oxidative damage. a The methylation of cytosine (filled circles) within CpG repeats to form methyl cytosine causes loss of affinity of the transcription factors for the promoter and silencing of the gene. b If the cytosines are not methylated (empty circles) due to lack of SAMe or if the methylation mark is lost due to de-methylation triggered by methyl cytosine oxidation, the gene is not anymore silenced and may undergo inappropriate expression. c If either the methyl cytosine or the guanosine of the CpG repeat are oxidised (small filled circles), the domain reverts from hydrophobic back to hydrophilic and the transcription factors recover the ability to bind and to express the gene in spite of the methylation of the CpG island. Both cases b and c lead to epigenetic instability