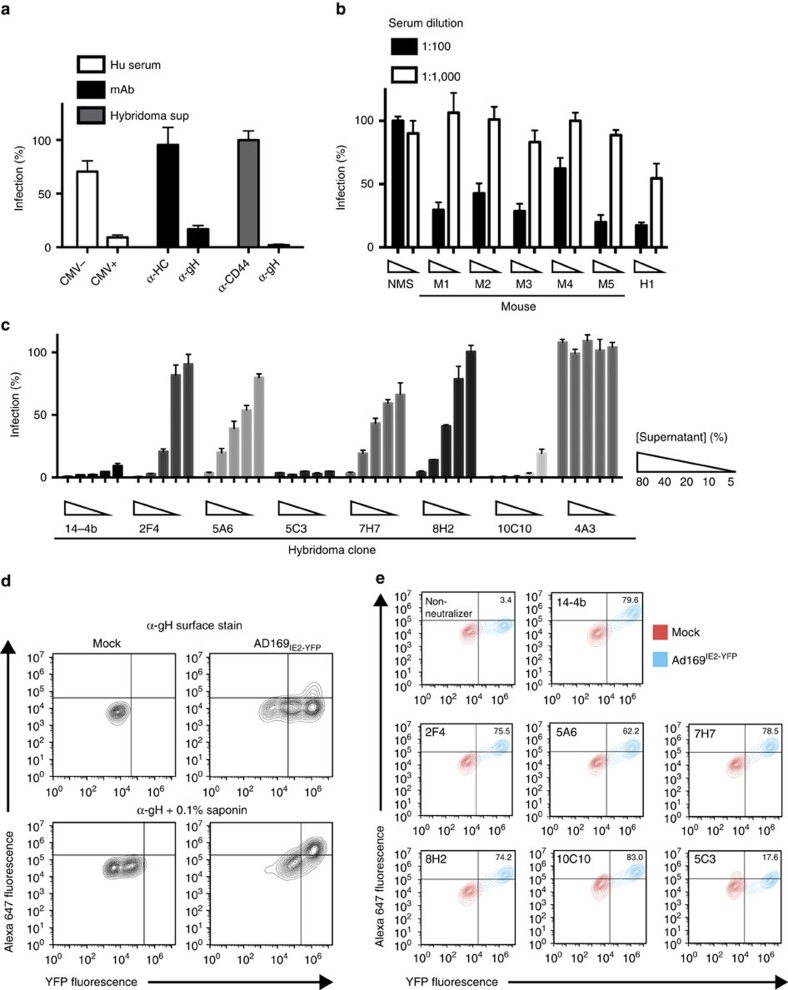
Figure 1. Identification of CMV-neutralizing mAbs using a HTN assay.
(a) Human serum, purified mAb (anti-MHCI heavy chain (HC) mAb (HC-10), anti-gH mAb 14-4b) and hybridoma supernatant were tested in a HTN assay for their ability to block infection of fibroblasts by AD169IE2-YFP. (b) Serum from mice inoculated with AD169 was tested for its ability to neutralize AD169IE2-YFP infection at 1:100 (black bars) or 1:1000 (white bars). Normal mouse serum (NMS) or CMV+ human serum (H1) were used as controls. (c) Hybridoma supernatant from 6 CMV-neutralizing clones was tested in 5-point dilutions (5–80%) for their ability to inhibit AD169IE2-YFP infection. Supernatant from the neutralizing anti-gH mAb 14-4b and supernatant from the non-neutralizing hybridoma clone 4A3 were utilized as controls. (d) MRC5 cells infected with AD169IE2-YFP were exposed to anti-gH (14-4b) flow cytometry staining without (top row) or with (bottom row) permeabilization with saponin. (e) Mock-infected MRC5 cells (red) or infected with AD169IE2-YFP (blue) were permeabilized and then exposed to hybridoma supernatant from the CMV-neutralizing clones followed by detection with flow cytometry. Experiments for (a–c) were performed in technical triplicate and s.d. is depicted.