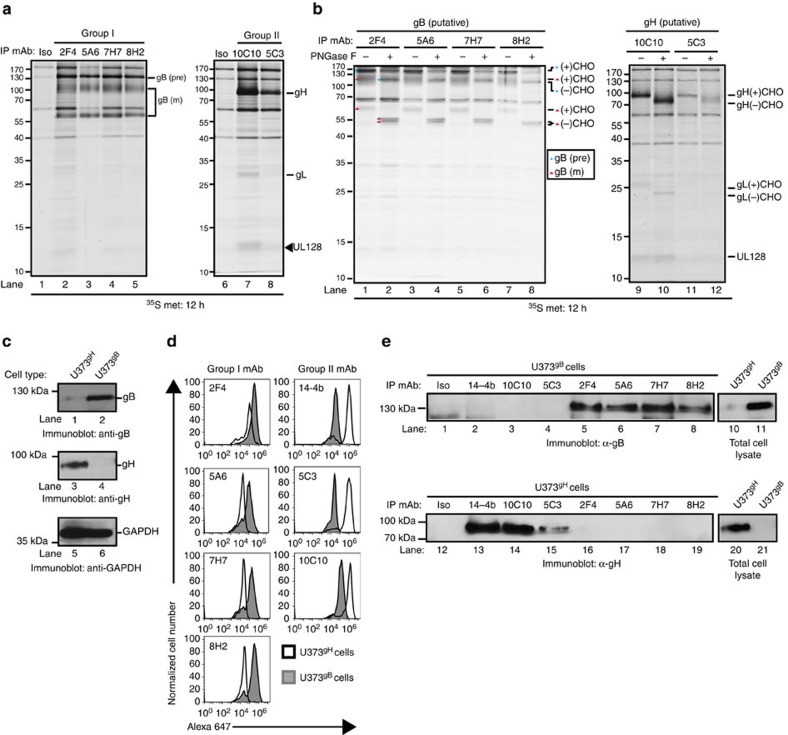
Figure 2. Identification of CMV-neutralizing mAb targets.
(a) Lysates from metabolically labelled AD169IE2-YFP-infected MRC5 cells were exposed to the CMV-neutralizing mAbs and recovered immune complexes were resolved by SDS–PAGE. Arrows denote the suspected peptide identity. (b) Immune complexes recovered from the metabolically labelled cell lysates were exposed to PNGase treatment and resolved by SDS–PAGE. Arrows denote the suspected peptide identity and glycosylation state. (c) Total cell lysates from U373 glioblastoma cells stably expressing gH (U373gH) or gB (U373gB) were resolved by SDS–PAGE and exposed to immunoblot for gB (lanes 1–2), gH (lanes 3–4) and GAPDH (lanes 5–6) proteins. (d) U373gH (white peaks) and U373gB (grey peaks) cells were permeabilized and exposed to the neutralizing CMV mAbs followed by detection with flow cytometry. mAb 14-4b was used as a positive control for labelling of the gH protein. (e) Total cell lysates from U373gB (lanes 1–8) and U373gH (lanes 12–19) were exposed to the CMV-neutralizing mAbs. The recovered immune complexes were resolved by SDS–PAGE and exposed to anti-gB (lanes 1–8) or anti-gH (lanes 12–19) antibody. Total cell lysates from U373gB (lanes 10–11) and U373gH (lanes 20–21) validated expression of the respective CMV protein in each cell type. Relative molecular mass markers are indicated in all relevant figures.