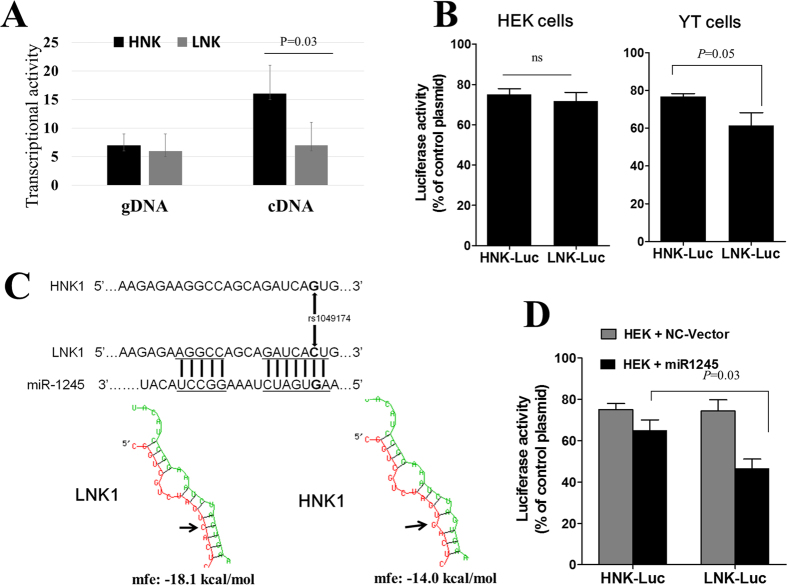
Figure 4. Molecular characterization of rs1049174 polymorphism in the 3′UTR of the NKG2D gene.
(A) Allele-specific transcriptional activity showing allelic imbalance. The HNK allele had higher transcriptional activity than the LNK allele in cDNA samples but not in gDNA samples from individuals heterozygous for the rs1049174 polymorphism. (B) Modulation of reporter gene expression by NKG2D 3′UTR polymorphism. YT cells and HEK cells were transfected with a luciferase expression vector pGL3 TK, or with constructs including the NKG2D 3′UTR HNK1-allele (pGL3 TK HNK1) or the LNK1-allele (pGL3 TK LNK1). The insertion of NKG2D 3′UTR segments repressed luciferase activity. The LNK allele construct, however, repressed the luciferase activity to a significantly greater degree in the YT transfected cells than in the miR1245-lacking HEK cells. (C) The rs1049174 SNP 3′UTR region of NKG2D occurs in the miR-1245 binding site, and miR-1245 is expressed in NK cells. A schematic representation of the location 1049174 SNP within the miR-1245 target site in the 3′UTR region of NKG2D. The presence of the HNK genotype (1163C) interrupts the pair-complementarity, decreasing the affinity between NKG2D mRNA and miR-1245. (D) The ectopic induction of miR1245 expression in HEK cells resulted in greater luciferase activity repression induced by the LNK allele. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with miR-1245 and pGL3 TK-Luc HNK or pGL3 TK-Luc vectors. At 48 h after transfection, the luciferase activity was measured. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to renilla luciferase expression, and the means ± the standard error of the percentage of activities in the control situation (cells transfected with luciferase plasmid without NKG2D 3′UTR) are shown.