Figure 9. Molecular mechanism of hypoxia-induced TRAIL resistance in colorectal cancer cells.
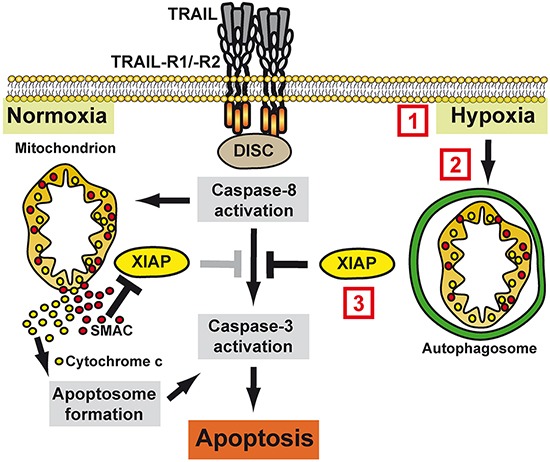
Under normoxic conditions, TRAIL-R1/−R2 activation triggers DISC assembly with subsequent caspase-8 activation. Mitochondria amplify the death signal via the release of pro-apoptotic factors such as cytochrome c and SMAC, which boost caspase-3 activation by initiating apoptosome formation and antagonizing XIAP, respectively. Under hypoxic conditions, mitophagy sequesters mitochondria-derived pro-apoptotic molecules, thereby blocking efficient apoptosis induction. Therapeutically, hypoxia-induced TRAIL resistance can be overcome by (1) increasing local oxygen levels (e.g. systemic hyperoxia or promoting angiogenesis), (2) inhibition of hypoxia-induced mitophagy (e.g. Bay87-2243 targeting HIF1α or 3MA blocking autophagosome formation) or (3) targeting XIAP (e.g. SMAC mimetics or blocking XIAP transcription using MithA).
