Figure 5. Enhancement of CTL activity against melanoma with the combination of CXCL2 and HVJ-E.
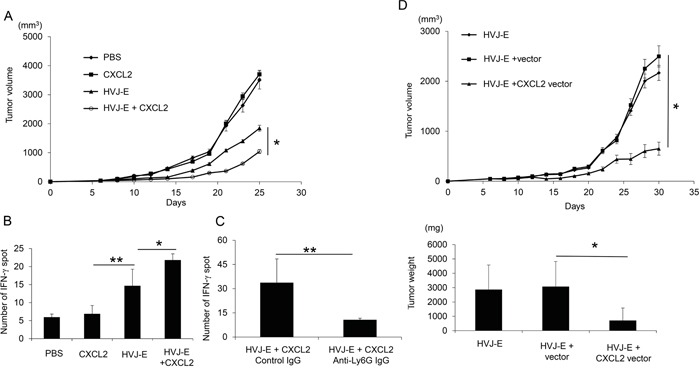
A. The anti-tumor effects of HVJ-E (2500HAU) combined with recombinant CXCL2 protein (0.3 ng/mouse) were evaluated in B16-F10 melanoma-bearing mice. The tumor volume on day 25 after tumor inoculation was compared for each treatment (n=6). * Indicates p<0.05. B. An Elispot assay with splenocytes against B16-F10 cells was performed (n=4). ** Indicates p<0.01, and * indicates p<0.05. C. The involvement of neutrophils in CTL activity against melanoma was examined. An anti-neutrophil antibody was intraperitoneally administered 24 hours before the intratumoral injection of HVJ-E+CXCL2 (2500HAU+0.3 ng/mouse) (n=4). Then, the Elispot assay with splenocytes against B16-F10 cells was performed. D. The effects of gene therapy using HVJ-E harboring a CXCL2 expression plasmid DNA (pCY4B-CXCL2) (50 μg/mouse) were examined in mouse melanoma. As a control, pCY4B without the CXCL2 cDNA (vector) was incorporated into HVJ-E. The tumor volume (upper graph) and isolated tumor weight (lower graph) on day 30 were measured (n=6). * Indicates p<0.05.
