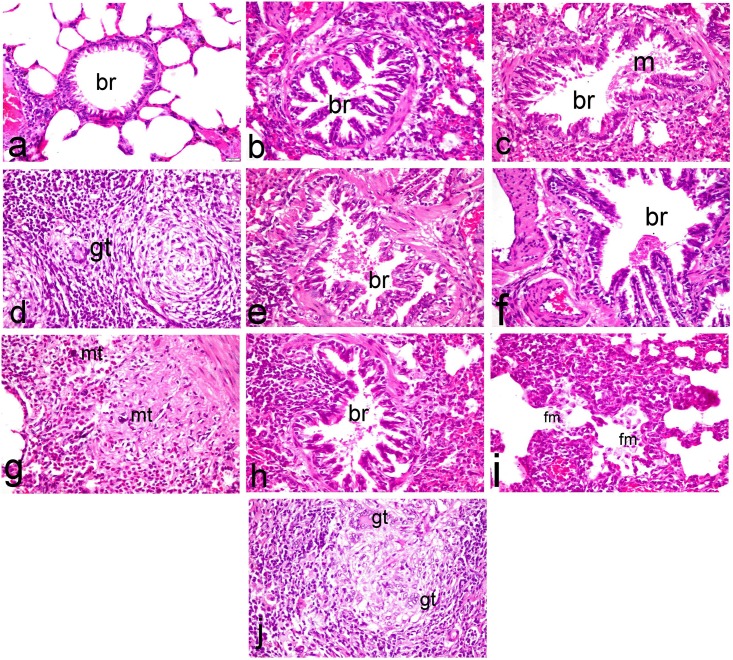
Fig 6. Histopathological investigation of lung tissues.
Lung sections of (a) normal rats showing normal pulmonary parenchyma with normal bronchiolar epithelium (br) and normal alveoli, (b) ipPDC-treated rats showing hyperplasia of the bronchiolar epithelium with peribronchiolar leukocytic cell infiltration, (c & d) inPDC (0.5 mg/kg)-treated rats showing (c) proliferation of bronchiolar epithelium associated with apoptotic changes and intraluminal aggregation of mucous materials (m) mixed with desquamated epithelium, (d) non-caseating granuloma with presence of giant cells (gt), (e) inPDC (1 mg/kg)-treated rats showing epithelial shedding and intraluminal aggregation of mucous, and (f, g, h, i & j) inPDC (2 mg/kg)-treated rats showing (f) papillary hyperplasia of bronchial epithelium, (g) intense infiltration of bronchial mucosa and bronchial wall with inflammatory cells concurrently with activation of mast cells (mt), (h) hyperplasia of the epithelial lining terminal bronchioles with intense peribronchilar leukocytic cell infiltration, (i) marked thickening of the alveolar wall with intraluminal aggregation of foamy macrophages (fm), (j) granuloma with aggregation of multiple giant cells of foreign type. (H&E, X40).