Abstract
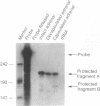
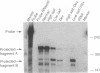
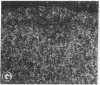
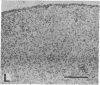
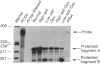
Adrenal mitochondria possess two steroidogenic cytochrome P450s. P450c11 converts deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone and aldosterone, and P450scc converts cholesterol to pregnenolone. These P450s receive electrons from NADPH via adrenodoxin reductase and adrenodoxin. A single bovine P450c11 protein has 11-hydroxylase, 18-hydroxylase, and 18-oxidase activities, but this series of enzymatic steps may be mediated by more than one enzyme in rats. Enzymatic assays of purified rat mitochondrial proteins have suggested that one enzyme found in all zones of the adrenal cortex has both 11- and 18-hydroxylase activities, whereas another enzyme, found exclusively in the zona glomerulosa, catalyzes 18-hydroxylation and 18-oxidation of corticosterone. We studied the number and zonal distribution of P450c11 mRNA species in the rat adrenal and how these mRNAs are regulated in the adrenals of normal and pregnant rats. Rats synthesize two similar, but distinct, P450c11 mRNAs. One, P450c11A, is found in both the zona glomerulosa and fasciculata/reticularis, whereas the second, P450c11B, is found only in the zona glomerulosa. The abundance of neither P450c11A mRNA nor P450c11B mRNA is affected by a high-salt diet. However, when rats receive a low-salt diet, P450c11A mRNA decreases and P450c11B mRNA increases. Dexamethasone decreases the amount of P450c11A mRNA without affecting P450c11B mRNA. The combination of a high-salt diet and dexamethasone decreases the amount of both mRNAs further to almost undetectable amounts. Rats given a low-salt diet and dexamethasone have a dramatic increase in the abundance of P450c11B mRNA. Thus both forms of P450c11 mRNA are regulated independently in the rat adrenal cortex. In situ hybridization studies show that only the P450c11 found in the zona glomerulosa is regulated by salt treatment in vivo, whereas glucocorticoid treatment in vivo regulates P450c11 in all zones. In the adrenals of pregnant rats, P450c11B is regulated in a similar fashion to its regulation in the nonpregnant rat adrenal, despite major differences in sodium retention and intravascular volume in pregnant and nonpregnant rats. In the pregnant rat, a low-salt diet increases the abundance of P450c11B to a greater degree than in the nonpregnant rat. By contrast, dexamethasone does not diminish the abundance of P450c11A mRNA in the pregnant rat but reduces it to an almost undetectable amount in the nonpregnant rat. Thus, the regulation of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid production in the pregnant and nonpregnant rat occurs by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barron W. M. Volume homeostasis during pregnancy in the rat. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987 Apr;9(4):296–302. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(87)80125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. A., Sinosich M. J., Saunders D. M., Gallery E. D. Potassium regulation and progesterone-aldosterone interrelationships in human pregnancy: a prospective study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Aug;155(2):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90824-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill S., Bengele H. H., Melby J. C., Alexander E. A. Role of aldosterone in sodium retention of pregnancy in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):R175–R181. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1981.240.3.R175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper C. F., Mellon S. H., Cumin F., Baxter J. D., Ganong W. F. Analysis by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization of renin and its mRNA in kidney, testis, adrenal, and pituitary of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7552–7556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörr H. G., Heller A., Versmold H. T., Sippell W. G., Herrmann M., Bidlingmaier F., Knorr D. Longitudinal study of progestins, mineralocorticoids, and glucocorticoids throughout human pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 May;68(5):863–868. doi: 10.1210/jcem-68-5-863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland H. O., Atherton J. C., Baylis C., Morgan M. R., Milne C. M. Hormone profiles for progesterone, oestradiol, prolactin, plasma renin activity, aldosterone and corticosterone during pregnancy and pseudopregnancy in two strains of rat: correlation with renal studies. J Endocrinol. 1987 Jun;113(3):435–444. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1130435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Globerman H., Rösler A., Theodor R., New M. I., White P. C. An inherited defect in aldosterone biosynthesis caused by a mutation in or near the gene for steroid 11-hydroxylase. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 3;319(18):1193–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811033191804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirita S., Morohashi K., Hashimoto T., Yoshioka H., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Omura T. Expression of two kinds of cytochrome P-450(11 beta) mRNA in bovine adrenal cortex. J Biochem. 1988 Nov;104(5):683–686. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauber M., Muller J. Purification and characterization of two distinct forms of rat adrenal cytochrome P450(11) beta: functional and structural aspects. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauber M., Sugano S., Ohnishi T., Okamoto M., Müller J. Aldosterone biosynthesis and cytochrome P-45011 beta: evidence for two different forms of the enzyme in rats. J Steroid Biochem. 1987 Jun;26(6):693–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)91041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukawa N., Nonaka Y., Ying Z., Higaki J., Ogihara T., Okamoto M. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAS encoding rat aldosterone synthase: variants of cytochrome P-450(11 beta). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 31;169(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91460-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Miller W. L. Extraadrenal steroid 21-hydroxylation is not mediated by P450c21. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1497–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI114325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Vaisse C. cAMP regulates P450scc gene expression by a cycloheximide-insensitive mechanism in cultured mouse Leydig MA-10 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7775–7779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Levine L. S. Molecular and clinical advances in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet E., Dupont J., Vitek A., White P. C. Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta). J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20961–20967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouw A. R., Rice D. A., Meade J. C., Chua S. C., White P. C., Schimmer B. P., Parker K. L. Structural and functional analysis of the promoter region of the gene encoding mouse steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1305–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J., Meuli C., Schmid C., Lauber M. Adaptation of aldosterone biosynthesis to sodium and potassium intake in the rat. J Steroid Biochem. 1989;34(1-6):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B. The P450 superfamily: updated listing of all genes and recommended nomenclature for the chromosomal loci. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka Y., Matsukawa N., Morohashi, Omura T., Ogihara T., Teraoka H., Okamoto M. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding rat adrenal cytochrome P-450(11)beta. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogishima T., Mitani F., Ishimura Y. Isolation of aldosterone synthase cytochrome P-450 from zona glomerulosa mitochondria of rat adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):10935–10938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle T. F., Kitay J. I. Ovarian and adrenal steroids during pregnancy and the oestrous cycle in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1977 Jul;74(1):89–98. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0740089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Wada A., Lauber M., Yamano T., Okamoto M. Aldosterone biosynthesis in mitochondria of isolated zones of adrenal cortex. J Steroid Biochem. 1988 Jul;31(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota K., Ota T., Yokoyama A. Plasma corticosterone concentrations and pituitary prolactin content in the pregnancy and their within-day fluctuations in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1974 Apr;61(1):21–28. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0610021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonino N., Levine L. S., Vecsei P., New M. I. Parallelism of 11 beta- and 18-hydroxylation demonstrated by urinary free hormones in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):557–560. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulick S. Diagnosis and nomenclature of the disorders of the terminal portion of the aldosterone biosynthetic pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jul;43(1):92–96. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISSER H. K., COST W. S. A NEW HEREDITARY DEFECT IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ALDOSTERONE: URINARY C21-CORTICOSTEROID PATTERN IN THREE RELATED PATIENTS WITH A SALT-LOSING SYNDROME, SUGGESTING AN 18-OXIDATION DEFECT. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1964 Dec;47:589–612. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0470589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Kulin H. E., Santen R. J., Wilson T. E., Melby J. C. Inborn error in the terminal step of aldosterone biosynthesis. Corticosterone methyl oxidase tpe II deficiency in a North American pedigree. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 17;303(3):117–121. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007173030301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Ohnishi T., Nonaka Y., Okamoto M., Yamano T. Synthesis of aldosterone by a reconstituted system of cytochrome P-45011 beta from bovine adrenocortical mitochondria. J Biochem. 1985 Jul;98(1):245–256. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanuki M., Tilley B. E., Hall P. F. Cytochrome P-450 for 11beta- and 18-hydroxylase activities of bovine adrenocortical mitochondria: one enzyme or two? Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):127–130. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp G. T., Coghlan J. P., Shulkes A. A., Skinner S. L., Wintour E. M. Regulation of aldosterone in the rat. Effect of oestrous cycle, pregnancy, and sodium status. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Oct;56(5):545–551. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Haniu M., Shively J. E., Shen W. H., Hall P. The synthesis of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex. Two zones (fasciculata and glomerulosa) possess one enzyme for 11 beta-, 18-hydroxylation, and aldehyde synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3556–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]