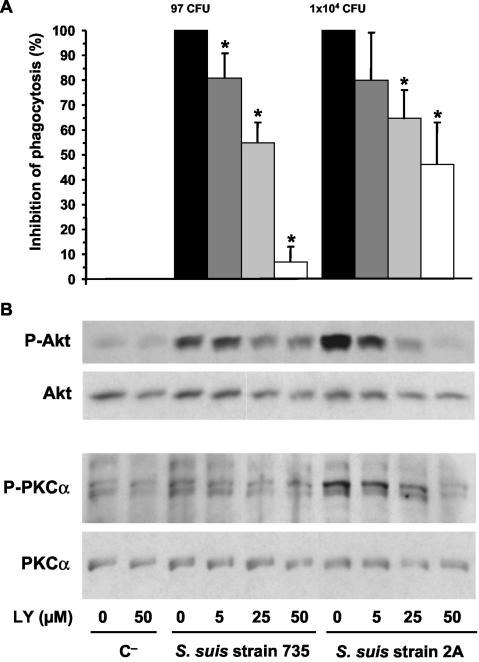
FIG. 2.
(A) S. suis phagocytosis inhibition by pretreatment of J774 macrophages with the PI-3K inhibitor LY-294002 (LY). Macrophages were pretreated 1 h before infection with 5, 25, or 50 μM doses of inhibitor (as indicated in the bottom panel of the figure). After 15 min of bacterial infection, phagocytosis inhibition was quantified by plating intracellular bacteria (encapsulated strain 735 and nonencapsulated mutant 2A) recovered from cell lysates, and the results are expressed as means ± the SD of the percent inhibition with respect to the phagocytosis values of untreated control cells (considered 100% phagocytosis and shown as CFU of recovered bacteria/milliliter in their corresponding histograms). An asterisk indicates a significant difference versus the untreated control cells (P < 0.01). (B) J774 macrophages were pretreated 1 h before infection with 5, 25, or 50 μM doses of inhibitor, and lysates obtained from noninfected control cells (C−) and 15-min-infected cells with encapsulated strain 735 and nonencapsulated mutant 2A were subjected to Western blotting. Akt and PKCα phosphorylation levels were revealed by using anti-Phospho-Akt (P-Akt) or anti-Phospho-PKCα (P-PKCα). Stripped filters were then reprobed with anti-Akt polyclonal antibody or anti-PKCα monoclonal antibody to confirm equal levels of protein. The results are representative of three individual experiments.