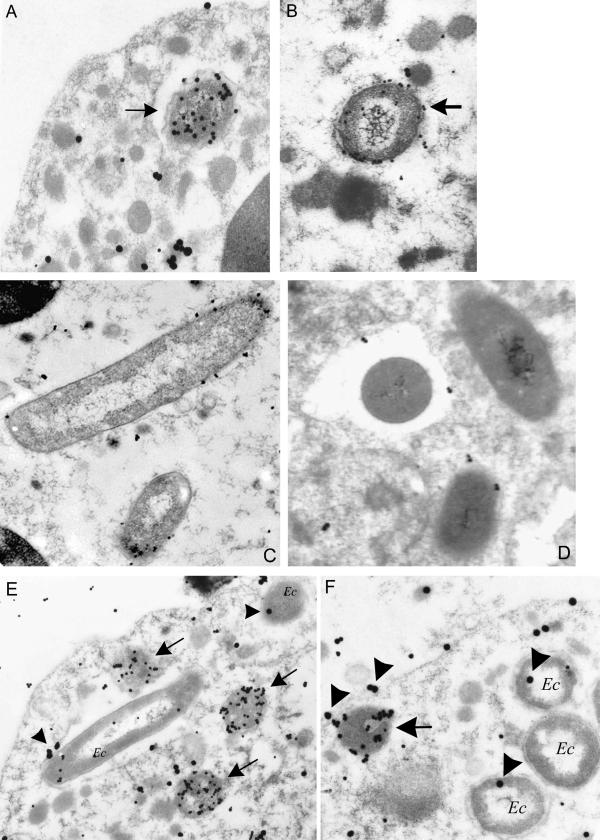
FIG. 6.
Electron microscopy of neutrophils incubated with A. phagocytophilum (A and B), E. coli (C and D), or both organisms simultaneously (E and F). Arrows indicate A. phagocytophilum-containing phagosomes. (A) Dual labeling with anti-A. phagocytophilum antibodies (small particles) and anti-gp91phox antibodies (large particles); (B) dual labeling with anti-A. phagocytophilum antibodies (small particles) and anti-p22phox antibodies (large particles); (C and D) single labeling (small particles only) of E. coli phagosomes labeled with anti-gp91phox (C) or anti-p22phox antibodies (D), respectively; (E) Neutrophils infected with A. phagocytophilum and E. coli (Ec), labeled with anti-A. phagocytophilum antibodies (small particles) and anti-gp91phox antibodies (large particles, indicated by arrowhead); (F) neutrophils infected with A. phagocytophilum and E. coli, labeled with anti-A. phagocytophilum antibodies (small particles) and anti-p22phox antibodies (large particles, indicated by arrowheads).