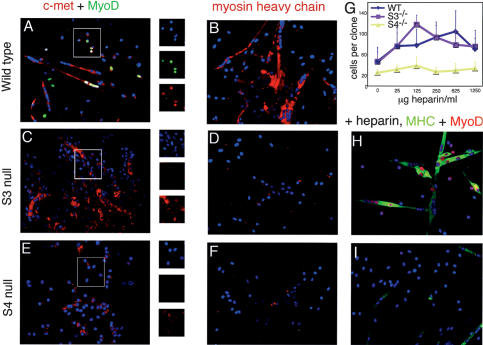
Figure 4.
Myogenesis in adherent colonies derived from fiber-associated satellite cells. Satellite cell colonies were stained for c-met (red) and MyoD (green; A,C,E) or marker myosin heavy chain (red; B,D,F); nuclei were visualized with DAPI. Wild-type colonies form multinucleate myotubes, stain positively for MyoD (A), and express myosin heavy chain, indicating successful differentiation (B). Syndecan-3-/- colonies form large, irregular syncytia, rarely express MyoD (C), and fail to express myosin heavy chain (D). Syndecan-4-/- colonies completely fail to either form myotubes or to express MyoD (E) and only very rarely do single cells express myosin heavy chain (F). (G) Addition of exogenous heparin increased the number of cells per clone in mass cultures of wild-type and syndecan-3-/- satellite cells but not syndecan-4-/- satellite cells; bars represent standard deviations. Heparin also increased differentiation as measured by expression of nuclear MyoD (red) and myosin heavy chain (green) in syndecan-3-/- cells (525 μg/mL shown; H) and partially rescued the mutant phenotype in syndecan-4-/- cells (525 μg/mL shown; I).