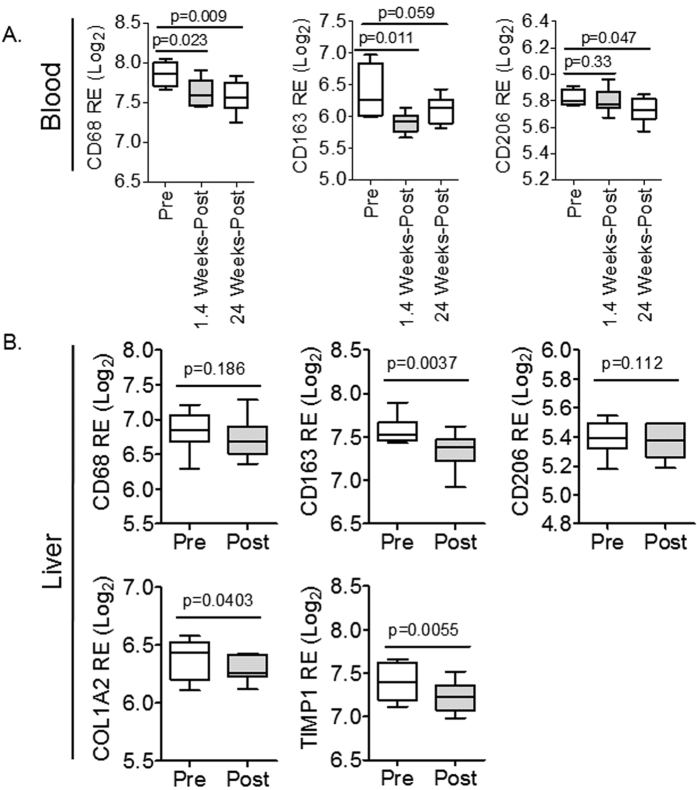
Figure 4. Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy is associated with reduced M2 macrophage activation genes and liver disease in chronic HCV-infected patients.
(A) Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy in chronic HCV patients is associated with reduced macrophage (CD68) and M2 macrophage markers (CD163, CD206) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) after 1.4 weeks (N = 8) and 24 weeks of therapy (N = 12), when compared to pre-treatment (N = 4). (B) DAA therapy results in attenuation of liver fibrogenesis (COL1A2, TIMP1), associated with significantly reduced CD163 mRNA levels in the liver, as examined in paired chronic HCV patients biopsies prior to (N = 8) and after (N = 8) treatment regimen (24 weeks of DAA therapy).