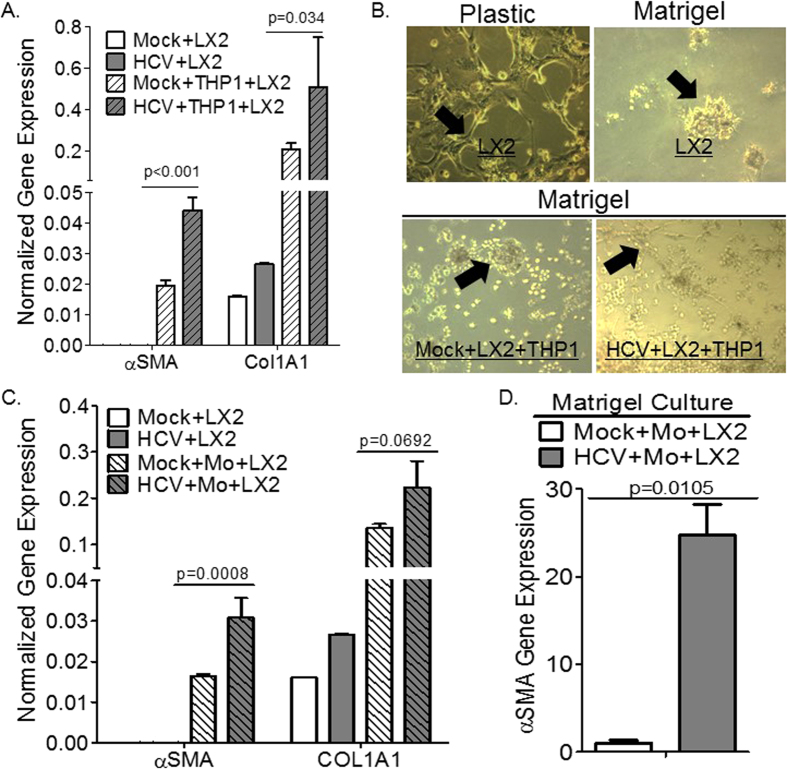
Figure 6. Human macrophages exposed to HCV promote hepatic stellate cell activation.
(A) Human monocytic cells (THP1) were cultured with supernatant from H77S.3/genotype 1 or JFH1/genotype 2-infected Huh7.5 cells or mock-infected Huh7.5 cells for 6 days, and subsequently co-cultured with human hepatic stellate cells (LX2) on plastic plates for 24 hours; fibrotic gene expression was examined by qPCR. (B) Human hepatic stellate cells (LX2 cells) cultured on Matrigel coated plates to induce cellular quiescence, were subsequently co-cultured with human monocytic cell line (THP1 cells) and supernatant from JFH1/genotype 2-infected Huh7.5 cells or from mock-infected Huh7.5 cells, and hepatic stellate cells activation was examined morphologically after 3 days (black arrows: quiescent cells phenotype - round clumps; while activated phenotype - fibroblast-like shape). (C) Primary human monocytes were cultured with supernatant from JFH1/genotype 2-infected Huh7.5 cells or mock-infected Huh7.5 cells for 6 days, and subsequently co-cultured with human hepatic stellate cells (LX2) on plastic plates for 24 hours; fibrotic gene expression was examined by qPCR. (D) Human hepatic stellate cell line (LX2), cultured on Matrigel coated plates to induce quiescence, were subsequently co-cultured with primary monocytes and supernatant from H77S.3/genotype 1-infected Huh7.5 cells or mock-infected Huh7.5 cells and hepatic stellate cell activation markers was analyzed after 3 days by gene expression.