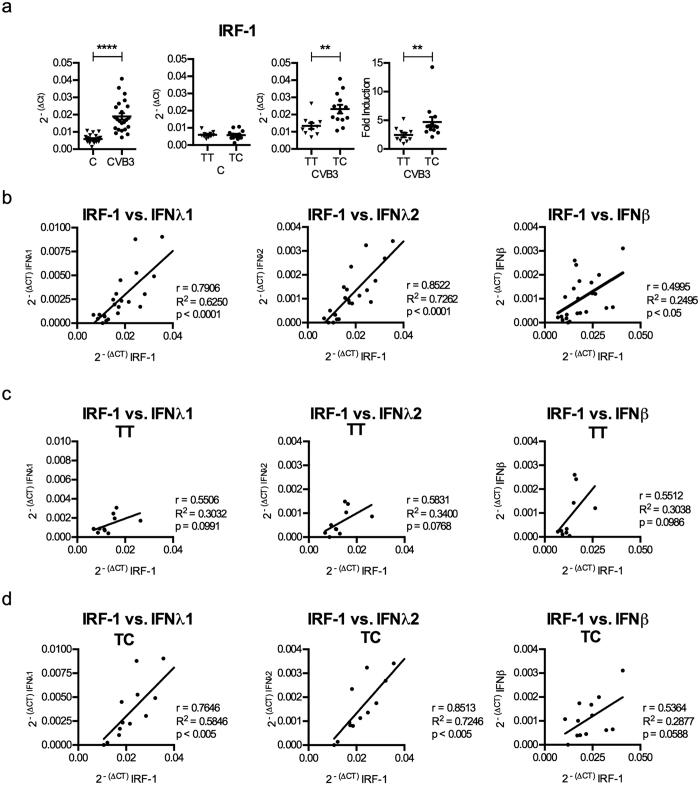
Figure 5. Higher expression levels of type III IFNs in TC donors correlate with the expression levels of the transcription factor IRF-1.
(a) mRNA expression levels of IRF-1 were measured at 48 h p.i. in the mock- and CVB3 infected islets described in Fig. 1 (n = 23) using quantitative real-time PCR. The expression levels were normalized to that of GAPDH and presented as 2−(ΔCt) (relative expression) for the whole islet cohort (first column). The results were re-analysed in that the donors were divided according to their rs1990760 genotype (TT or TC). The expression levels in the mock infected (C, second column) and CVB3 infected human islets (CVB3, third column) were normalized to that of GAPDH and presented as 2−(ΔCt) (relative expression), or normalized to GAPDH and compared to the expression levels in mock-infected islets from the same donor and presented as 2−(ΔΔCt) (fold induction: fourth column). (b) Correlation analysis was performed by comparing the mRNA levels for selected genes expressed by CVB3 infected islets at 48 h p.i. (n = 23). The 2−(ΔCt) values of IRF-1 were correlated with that of IFNλ1, IFNλ2 and IFNβ in CVB3 infected islets. (c,d) The correlations described in (b) were separately performed for donors with the rs1990760 TT (c) and TC (d) genotypes. Linear regression and the correlation coefficient r, R2 and p values were calculated using Pearson correlation test (b–d). p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.