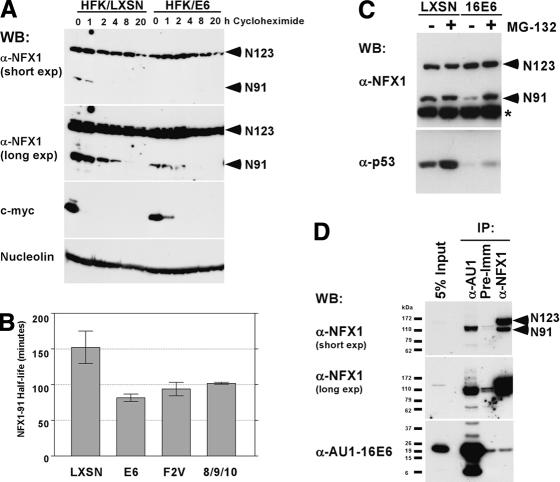
Figure 4.
NFX1-91 rather than NFX1-123 is targeted by the E6/E6-AP complex. (A) Western blot. HFK/LXSN and HFK/E6 cells were treated with 25 μg/mL cycloheximide for the indicated time points. Lysates were assayed for NFX1 expression levels using an affinity-purified NFX1 antibody. c-Myc is shown as a positive control for a short-lived protein. Nucleolin is a stable protein used as a loading control. (B) Half-life of NFX1-91. A pulse-chase experiment to calculate the half-life of NFX1-91 was performed using metabolically labeled HFKs expressing the indicated E6 construct or LXSN vector control. The data presented are the average of two or three independent experiments for each cell line. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (C) Decreased expression of NFX1-91 seen in E6-expressing HFKs was proteasome dependent. Proteasome inhibition with MG-132 restored NFX1-91 protein levels. NFX1 protein was detected using an IgG-purified NFX1 antibody. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific background band used as a loading control. p53 expression is shown as a control for proteasome inhibition. (D) Endogenous NFX1-91 coimmunoprecipitated with AU1-tagged 16E6 in transiently transfected 293T cells. A longer exposure of the NFX1 blot shows the presence of a ubiquitin ladder. The reciprocal IP to precipitate AU1-16E6 with NFX1 antibody did not work.