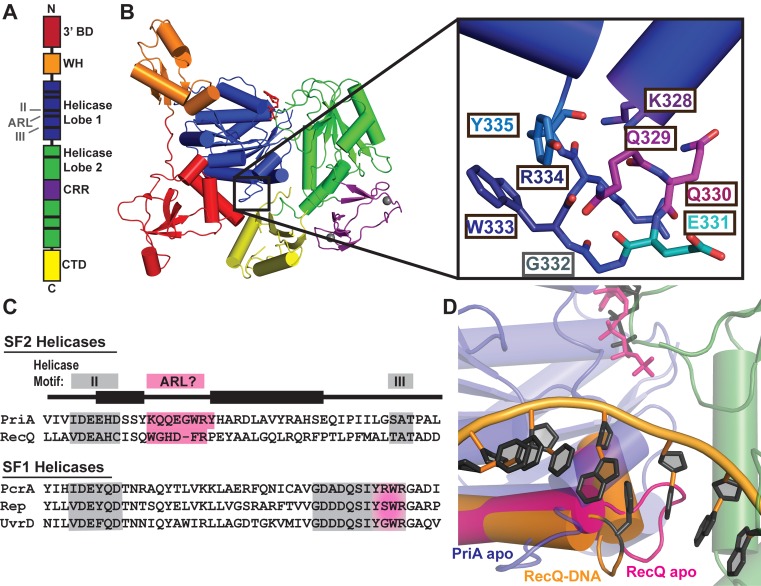
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of PriA reveals an aromatic-rich loop (ARL) at a similar location within the helicase lobes as the ARL of RecQ. (A) Schematic PriA domain structure highlighting the positions of helicase motifs (black bars). (B) Klebsiella pneumonia PriA structure (PDB 4NL4 (23)) with ADP (red sticks) and zinc (grey spheres) bound. Domain coloring for 3′ binding domain (3′BD), winged helix (WH), helicase lobes, cysteine-rich region (CRR) and C-terminal domain (CTD) is the same in both images. Inset: PriA ARL residue side chains. (C) Sequence alignment of helicase motif II-III (grey) in K. pneumonia PriA, Cronobacter sakazakii RecQ and representative SF1 helicases. Pink highlighting corresponds to proposed ARL sequences, including the C-terminal portion of motif III in SF1 helicases. (D) Structural alignment of the helicase lobes for PriA (colored as in B, with ADP in grey sticks) with RecQ: ARL from ATPγS-bound apo E. coli RecQ in magenta (PDB 1OYY (34)) and ARL from partial duplex DNA-bound C. sakazakii RecQ in orange with DNA rings and base-stacking phenylalanine shown in black (PDB 4TMU (13)).