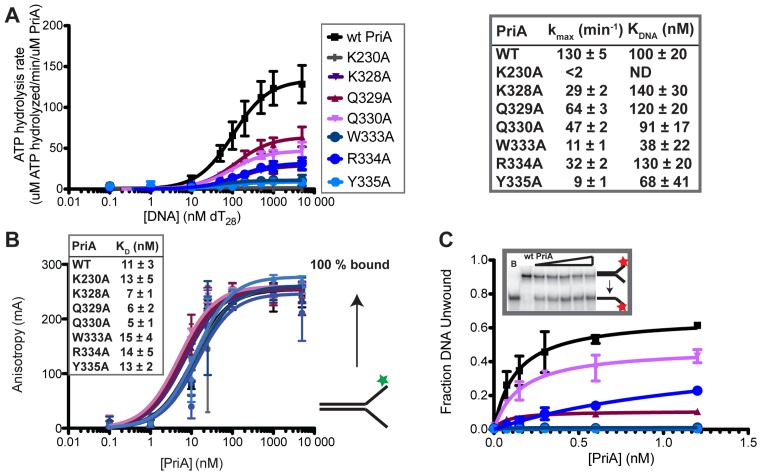
Figure 2.
Alanine substitutions within the PriA ARL reduce PriA ATPase activities. (A) Coupled spectrophotometric ATPase assay monitoring DNA-dependent ATP hydrolysis. kmax and KDNA are shown for each PriA variant. K230A is a Walker A mutant used as a negative control for ATPase and helicase activity in this study. (‘ND’ indicates none detected). (B) Equilibrium binding of PriA variants to a 5′-fluorescein labeled DNA (depicted to right: the DNA is comprised of two DNA oligonucleotides with 60 nt of complementary DNA and 38 nt of non-complementarity (structure #1 in Supplementary Table S1)). Inset shows apparent KD derived from fits to a single-site binding model. (C) DNA helicase assay measuring unwinding of 1 nM 5′ 32P-labeled DNA fork (as in part B: Supplementary Table S1 structure #1) by PriA variants. Inset shows example PAGE (lanes: Boiled DNA, 0, 0.15, 0.3, 0.6 and 1.2 nM PriA) and graph shows quantification of unwound DNA band. All data are mean of a minimum of three replicates ± SD.