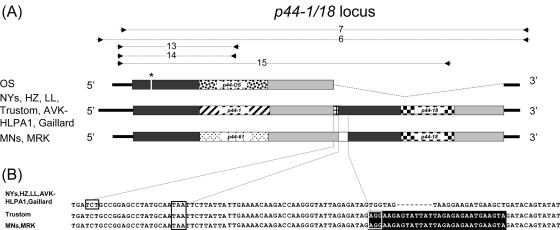
FIG. 2.
Comparison of p44-1/18 genomic loci in geographically different isolates. (A) Schematic diagram of p44-1/18 genomic loci. p44-1, p44-18, p44-61, p44-MRK, and p44-OS hv regions are shown by different fill patterns. Flanking conserved regions are shown as gray bars. The p44-1 and p44-18 overlap region in northeastern isolates is shown as a small grid. p44-61 and p44-18 are separated by a 37-bp intergenic space in the p44-61/18 locus in Minnesota strains (white box). Primer set 6 was used to amplify the p44-1/18 locus in all northeastern strains; primer set 7 was used to amplify the p44-1/18 locus equivalents in the Minnesota, MRK, and OS strains. Primer sets 13 to 15 were used in transcriptional analysis of this locus. Amplicons are shown above the genetic map; the in-frame stop codon in p44-OS is shown by an asterisk. (B) Sequence comparison of the p44-1 (p44-61) and p44-18 junction in different United States isolates. Nucleotides shown on a black background are identical in the Minnesota, MRK, and Trustom strains. The boxed nucleotides (TCT) shown are the first in-frame codon of p44-18. The boxed nucleotides TAA are the stop codon for p44-1 in northeastern strains and for p44-61 in Minnesota and MRK strains. The boxed nucleotides with black background indicate the first in-frame codon (AGG) of p44-18. Gaps are shown by dashes.