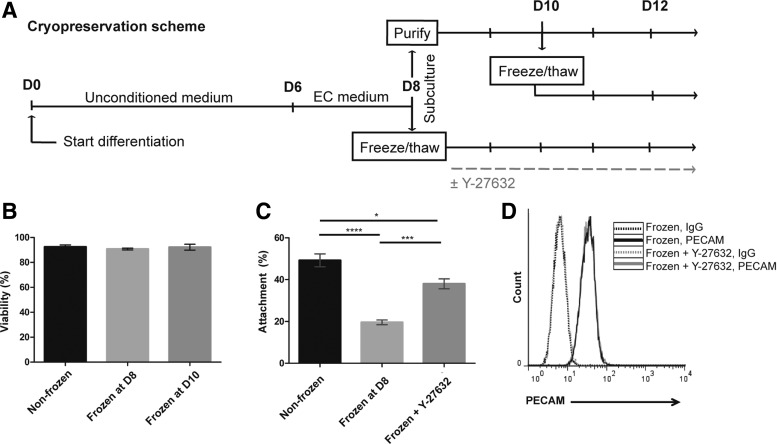
FIG. 1.
Viability, yield, and purity of cryopreserved iPSC-BMECs. (A) Timeline of cryopreservation scheme. Cells were cryopreserved at D8 of differentiation during routine subculture or at D10 as purified iPSC-BMECs. (B) Viability of cryopreserved IMR90-4 iPSC-BMECs as measured by Trypan blue staining. Data are average ± standard deviation from at least three independent differentiations. (C) Percent attachment of cryopreserved IMR90-4 iPSC-BMECs with or without 10 μM Y-27632 treatment, calculated as the number of cells attached at 24 h post-thaw normalized to number of cells seeded at 0 h. Data represent the average ± standard deviation from triplicate samples from one independent differentiation, and experiments were repeated for an additional differentiation to verify trends. Statistical significance was calculated through ANOVA (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). (D) Purity of cryopreserved IMR90-4 iPSC-BMECs as assessed by PECAM flow cytometry. Cells were cryopreserved at D8 of differentiation, and PECAM flow cytometry was performed 24 h post-thaw, with or without 10 μM Y-27632 treatment. ANOVA, analysis of variance; BMECs, brain microvascular endothelial cells; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell.