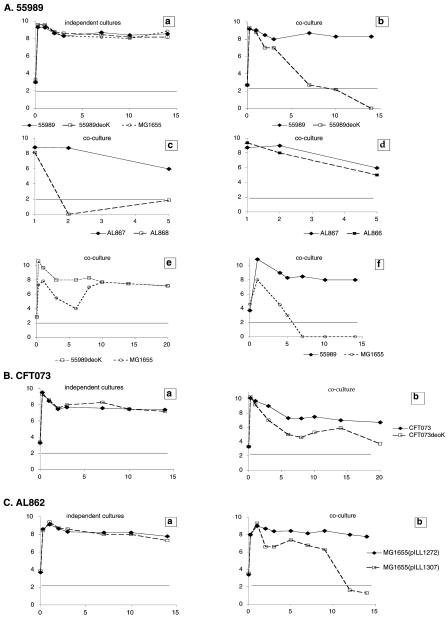
FIG. 2.
Experiments conducted with isolates 55989 (A) and CFT073 (B) and with isolate MG1655 carrying the deoK operon from AL862 (C). Bacteria were grown separately or in coculture for 2 to 3 weeks. Samples were taken periodically, and viable counts were determined by plating out serial dilutions on Luria-Bertani agar supplemented with antibiotic or not, as appropriate. Each assay was performed at least twice. The detection limit of the titration method is <100 CFU/ml. Wild-type strains were cocultured with their respective deoK mutants (Ab, Bb, and Cb). Similar results were obtained in coculture experiments with either the parental 55989 isolate or its Nal derivative. The 55989deoK mutant was transcomplemented with the cloned deoK gene (AL866) and cocultured with AL867 (Ad; compare to Ac as a negative control). Strain 55989 carrying the deoK operon or without it was also cocultured with the commensal strain MG1655 (Af or Ae, respectively). Cocultures were performed with the parental 55989 and MG1655 isolates, the 55989 Nal and MG1655 Rif derivatives, or the 55989 Rif and MG1655 Nal derivatives. Similar results were also obtained when 55989 Nal was cocultured with MG1655 Rif at a 1:100 ratio.