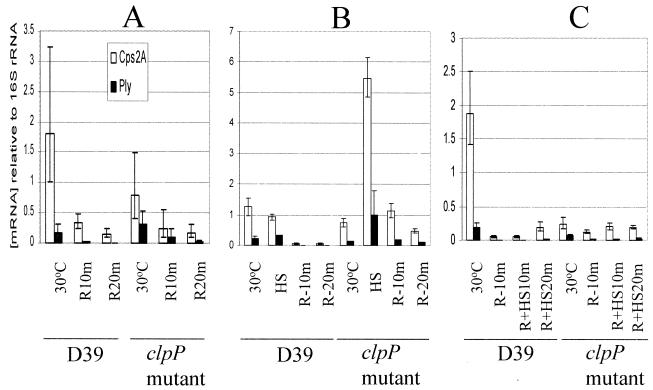
FIG. 1.
Detection of relative mRNA stabilities of cps(2)A and ply by real-time RT-PCR. (A) To determine the mRNA half-lives at 30°C, S. pneumoniae strains were grown at 30°C, and then rifampin was added. Aliquots for RNA extraction were withdrawn before the addition of rifampin and at 10 and 20 min after rifampin was added (R10m and R20m, respectively). (B) To determine the mRNA half-lives after heat shock, S. pneumoniae strains were grown at 30°C and then heat shocked (HS) at 42°C. After 10 min at 42°C, rifampin was added. Aliquots for RNA extraction were withdrawn before and after heat shock and at 10 and 20 min after the addition of rifampin at 42°C. (C) To determine the effect of heat shock on the mRNA half-lives, S. pneumoniae strains grown at 30°C were treated with rifampin for 10 min and then heat shocked at 42°C. Aliquots for RNA extraction were withdrawn before and at 10 min after the addition of rifampin at 30°C (R-10m) and then at 10 and 20 min after heat shock (R+HS10m and R+HS20m, respectively). Between RNA extracts, levels of individual mRNA species were corrected by reference to that obtained for the internal 16S rRNA control. Data points represent means and standard deviations of quadruplicate samples from each RNA extract.