Figure 1.
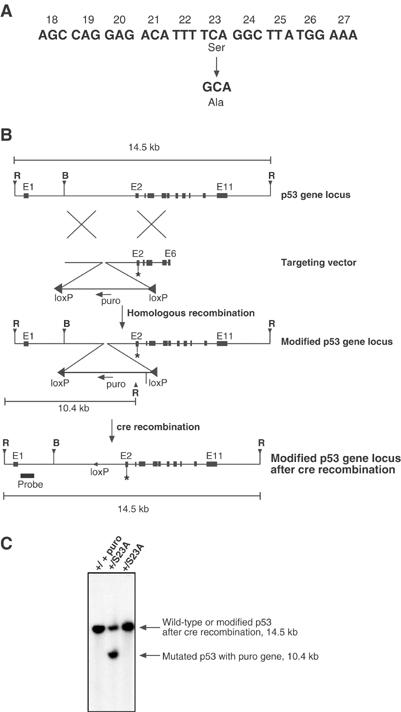
Targeting of endogenous p53 locus to introduce a Ser23 to Ala mutation. (A) The S23A mutation that is introduced by a single-nucleotide substitution is represented. (B) Schematic representation of targeting strategy. The targeting construct introduces the exon 2 point mutation and also introduces into intron 1 a puromycin cassette in the reverse orientation flanked by loxP (◂) sites, and containing an EcoR1 site. The modified p53 locus following homologous recombination is also shown. Following homologous recombination, Cre recombinase was introduced by transient transfection to delete the Puro cassette, leaving a single loxP site. The position of the probe external to the targeting cassette is shown, and the EcoR1-cut sites, internal and external to the cassette, are also indicated. Abbreviations used are: R, EcoR1; B, BamH1; puro, puromycin-resistance gene. (C) Genotyping of ES cell clones that survived puromycin selection. Southern blot analysis was performed on EcoR1-digested genomic DNA. The probe hybridizes to a 14.5 kb EcoR1 fragment from the unmodified locus (+/+). Correctly targeted heterozygous ES cells surviving puromycin selection also show the 10.4 kb EcoR1 fragment (+/S23Apuro). Following the addition of Cre to the targeted ES cell, the Puro cassette is excised (+/S23A).
