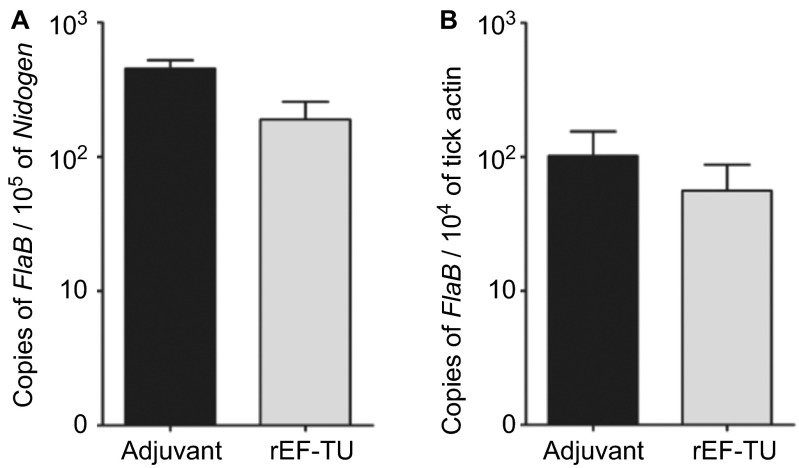
Figure 2.
Active immunization with rEF-Tu does not protect mice from B. burgdorferi, and anti-EF-Tu antibody does not affect spirochetal survival and migration in in the tick vector. (A) Quantitation of spirochete load in mice. Tibio-tarsal joints from mice immunized with rEF-Tu or non-immunized mice (labeled as ‘Adjuvant') were subjected to qPCR analyses (n = 4 mice/group). The B. burgdorferi flaB gene was used as target, and the levels were normalized with the mouse Nidogen gene. Data denote the mean ± the standard error (SEM) from two separate experiments. Differences between mice immunized with rEF-Tu and controls were analyzed using a Student t test (P value ≤ 0.05). (B) qPCR analyses of spirochete load in larvae fed on B. burgdorferi-infected mice that were either immunized with EF-Tu (which contains high levels of anti-EF-Tu antibodies) or non-immunized. Bars represent the mean ± SEM from 18 fed larval ticks collected from immunized mice and 9 fed larval ticks collected from controls (n = 2 mice/group). Data are representative of two separate experiments. Copies of the flaB genes were normalized with tick actin gene.