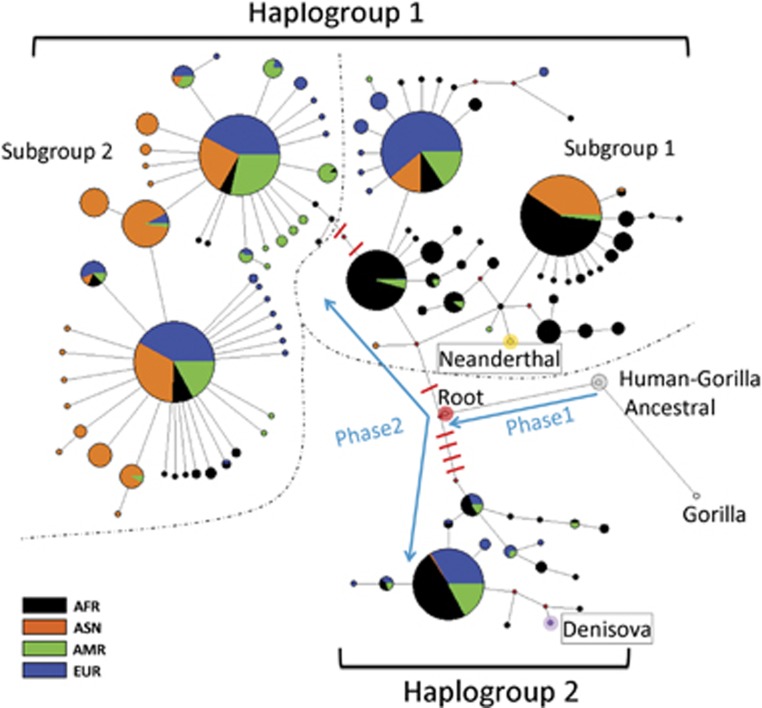
Figure 4.
Haplotype network of archaic and modern human IL37 haplotypes. A total of 119 haplotypes, including 114 modern human, 1 common ancestor of modern human, 2 archaic human, 1 gorilla and 1 human–gorilla ancestor haplotypes, were included for network construction. The sequence of common ancestor of modern human was deduced as described in method section and included to facilitate median-joining network construction. Gorilla and human–gorilla ancestral haplotypes were used to calibrate the molecular clock for evolution time estimation. Node labeled as ROOT (expanded red colored) corresponds to the reconstructed human common ancestor. The human haplotypes are divided into haplogroups 1 and 2 by a long branch with five non-synonymous substitutions. Dashed lines delineate two subgroups of haplogroup 1, which is separated by two non-synonymous substitutions. Phase 1 and phase 2 indicate two phases of hominid evolution after human–gorilla split. Non-synonymous substitutions only occurred at phase 2. Other nodes are labeled as indicated.