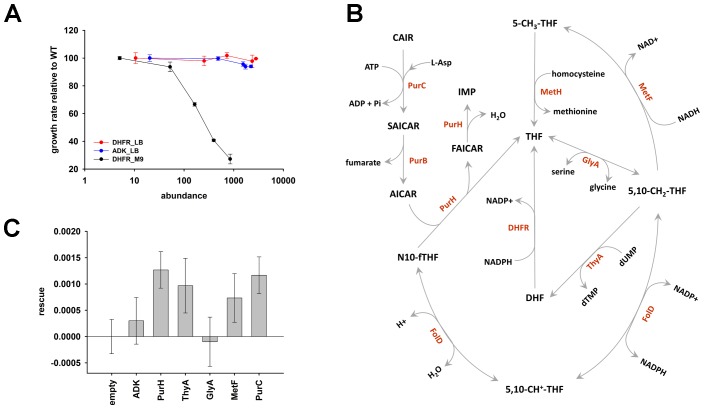
Figure 6. The role of purine biosynthesis and 1-carbon metabolism enzymes in DHFR over-expression toxicity.
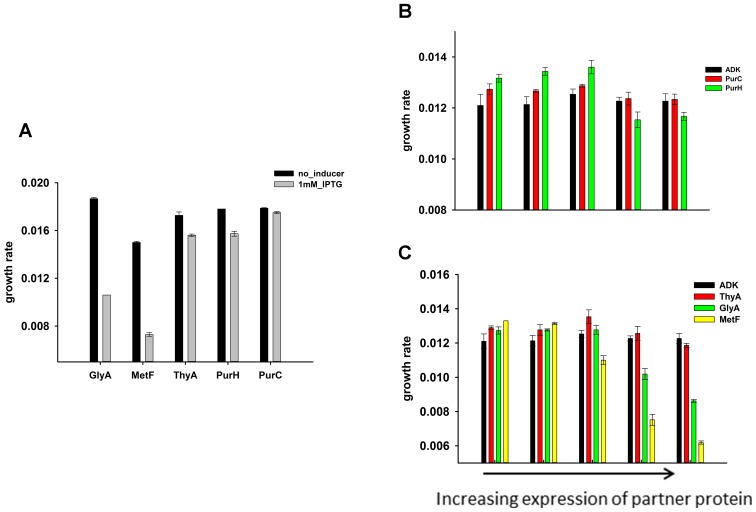
(A) Unlike supplemented M9 medium, over-expression of DHFR is not toxic in rich medium (LB) in terms of growth rate (Spearman r = −0.3, p=0.7), (note, however, that saturation ODs at 600 nm is lower in LB in comparison to growth in M9; see Figure 6—figure supplement 1). This indicates the role of conditionally essential genes like purH, purC, metF, etc. in determining the over-expression toxicity of DHFR. All data were normalized by growth rate of E. coli transformed with the empty plasmid. (B) Schematics of the 1-carbon pathway metabolic pathway. GlyA, ThyA, MetF are important enzymes that function immediately downstream of DHFR and utilize THF or its derivative. (C) Partial rescue of fitness of DHFR over-expressing E. coli by a dual-expression system. DHFR was expressed from a IPTG-inducible plasmid while PurH, ThyA, GlyA, MetF and PurC along with a negative control protein ADK were expressed separately from an arabinose-inducible pBAD system. Rescue factor is defined as , where is the growth rate, and X is the corresponding protein.