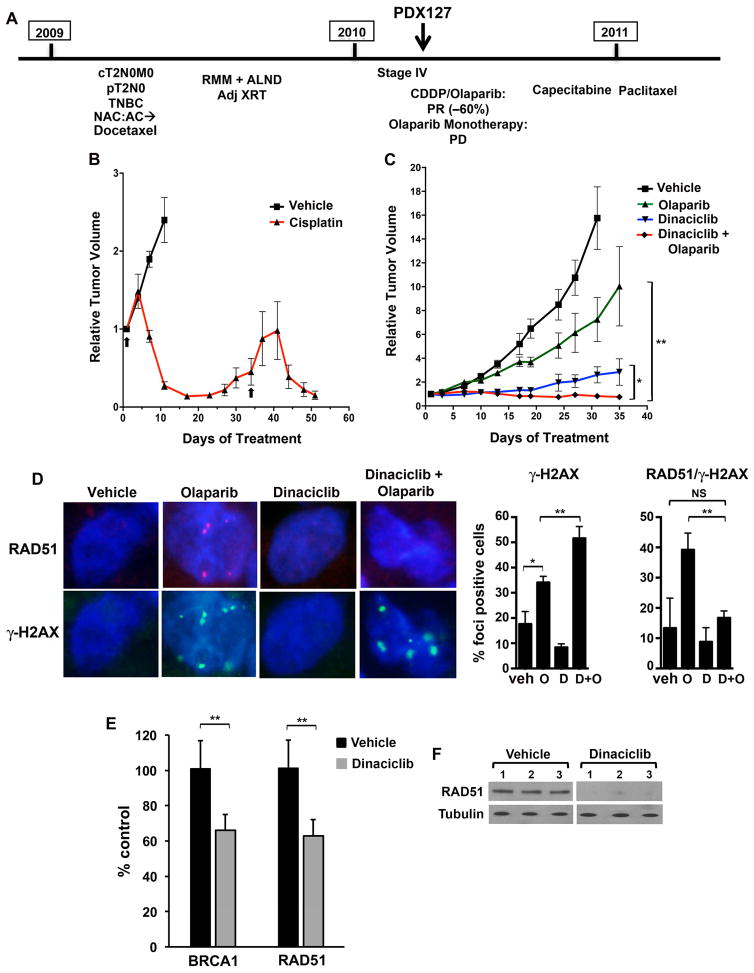
Figure 6. Generation and treatment of the PDX127 model from a 185delAG BRCA1 carrier.
(A) Treatment history of the BRCA1 carrier; the model was procured prior to exposure to cisplatin/olaparib or olaparib monotherapy. PR, partial response; PD, progressive disease. (B) Mice bearing xenografts were treated with vehicle (n = 4) or cisplatin (n = 6) on the days 1 and 34 (arrows) demonstrating tumor regression in response to platinum-based treatment. (C) Mice bearing xenografts were treated with vehicle (n = 8), olaparib (n = 7), dinaciclib (n = 3) or the combination (n = 7). Combination treatment produced significant tumor growth inhibition compared to vehicle or monotherapies. At day 35, P = 0.018 (*) for combination vs. dinaciclib and P < 0.0001 (**) for combination vs. olaparib. (D) Mice bearing xenografts were treated with vehicle, olaparib, dinaciclib or the combination (n = 6/group). (Left) After 15 days, mice were sacrificed and tumors subjected to immunofluroescence for RAD51 and γ-H2AX foci. (Right) Quantification of cells with > 5 γ-H2AX foci, as well as γ-H2AX-positive cells with > 5 RAD51 foci. For γ-H2AX foci, P values for control vs. dinaciclib, olaparib or the combination are 0.103, 0.013 (*) and 0.005, respectively. P values for dinaciclib or olaparib vs. the combination are < 0.0001 and 0.0076 (**), respectively. For RAD51 quantification in γ-H2AX-positive cells, P values for control vs. dinaciclib, olaparib or the combination are 0.69, 0.04 and 0.74 (NS), respectively. P values for dinaciclib or olaparib vs. the combination are 0.158 and 0.0035 (**), respectively. (E) Tumor RNA from mice in D treated with vehicle or dinaciclib (n = 3/group) was subjected to RT-PCR for BRCA1 and RAD51. P values for vehicle vs. dinaciclib are 0.000068 (**) in both cases. (F) Tumor lysates from mice in D treated with vehicle or dinaciclib were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies.